| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | New 500 kV Shunt Reactor |
| Rated voltage | 500KV |
| Series | SR |
Description:
Shunt reactors are connected in a parallel configuration to the power system to compensate for capacitive reactive power of transmission and distribution systems. This ensures that operating voltages are maintained within acceptable operating levels.
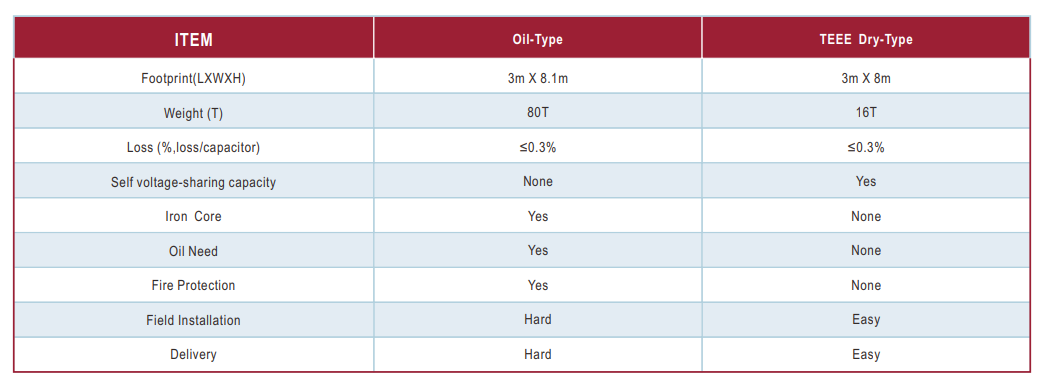
Shunt reactors are constructed as either “Oil-Immersed ” or “Dry-Type”.
Dry-Type reactors consist only of encapsulated windings, supported by the appropriate insulators.
Feature:
Special “Modular” Design which is more compact.
Good voltage equalizing performance, excellecnt tolerance to transient overvoltage.
No iron core, low vibration, low noise.
Only 20% of the weight of oil reactor, less occupation of land, completely replace the oil reactor, maintenance-free.
Low heat generation, rain proof, bird proof, good weather resistance and more reliable.
Easy assembly and disassembly, fast and convenient transportation, great anti-seismic structure.
Replaces Oil-Immersed shunt reactors and traditional Dry-Type Shunt Reactors.
Parameters:
How does a dry shunt reactor work?
In weak electrical systems, when the short-circuit power is relatively low, voltage increases due to capacitive generation. As the network's short-circuit power increases, the magnitude of voltage increase decreases, thereby reducing the need for compensation to limit overvoltage.
Reactors can achieve reactive power balance across different parts of the network. This is especially important in heavily loaded networks where new lines cannot be constructed due to environmental reasons. Reactors used for this purpose are mostly thyristor-controlled to rapidly adapt to the required reactive power. For instance, in industrial areas with arc furnaces, reactive power demand fluctuates between each half-cycle. Typically, a combination of Thyristor-Controlled Reactors (TCR) and Thyristor-Switched Capacitor banks (TSC) is used to absorb and generate reactive power based on instantaneous demand.
During single-phase reclosing in long transmission lines, interphase capacitive coupling can provide a current that sustains the arc, known as the secondary arc. By adding a single-phase reactor at the neutral point, the secondary arc can be extinguished, improving the success rate of single-phase automatic reclosing.