Transformer Vector Group Definition
The transformer vector group denotes the phase difference between the primary and secondary sides of a transformer, while also defining the arrangement of high-voltage and low-voltage windings in three-phase transformers. Vector groups are determined by the connection configurations of three-phase transformers, which can be categorized into four main groups based on the phase difference between corresponding line voltages of the high-voltage and low-voltage sides.
The phase difference—defined as the angle by which the low-voltage line voltage lags the high-voltage line voltage, measured in 30° increments clockwise—establishes the following groups:
- Group 1: No phase displacement
- Group 2: 180° phase displacement
- Group 3: (-30°) phase displacement
- Group 4: (+30°) phase displacement
For example, the connection Yd11 specifies:
- "Y" = High-voltage windings in star configuration
- "d" = Low-voltage windings in delta configuration
- "11" = Low-voltage line voltage lags high-voltage line voltage by 11×30°=330°(clockwise from the high-voltage phasor).
Clock Method for Phasor Difference Measurement
The clock method visualizes phase differences as clock dial positions:
- High-voltage windings = Minute hand
- Low-voltage windings = Hour hand
- 30° (the angle between adjacent clock dial numbers) serves as the unit of phase shift.
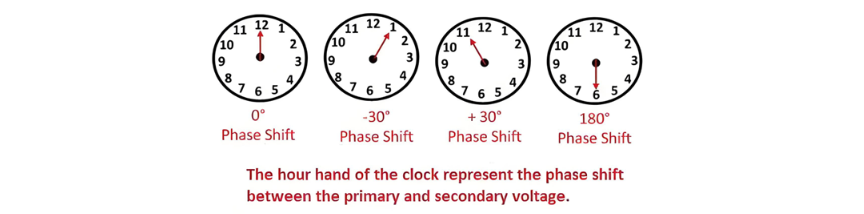
Clock Method Phase Displacement Interpretation
- When the hour hand points to 12, the phase displacement is 0°.
- At hour position 1, the phase shift is -30°.
- At hour position 6, the phase shift equals 6×30°=180°.
- At hour position 11, the phase shift is 11×30°=330°.
The group reference numbers (0, 6, 1, 11) denote primary-to-secondary phase shifts corresponding to clock hours. For instance, a Dy11 connection (delta-star transformer) indicates the low-voltage line phasor at hour 11, which is +30° phase-advanced relative to the high-voltage line voltage.
Parallel Connection Requirement
Key Note: Only transformers within the same vector group can be connected in parallel.
- Examples:
- Star-star (Y-Y) transformers can parallel with other Y-Y or delta-delta (∆-∆) transformers.
- A ∆-∆ transformer cannot be paralleled with a Y-∆ transformer due to incompatible phase shifts.