What is Differential Voltmeter ?
What is Differential Voltmeter ?
Definition: A voltmeter that measures the difference between a known voltage source and an unknown voltage source is called a differential voltmeter. It operates based on the principle of comparing the reference voltage source with the unknown voltage source.
The differential voltmeter offers very high accuracy. Its operating principle is similar to that of a potentiometer, and thus it is also known as a potentiometer voltmeter.
Construction of Differential Voltmeter
The circuit diagram of the differential voltmeter is shown below. A null meter is placed between the unknown voltage source and the precision divider. The output of the precision divider is connected to the known voltage source. The precision divider is adjusted until the null meter shows zero deflection.
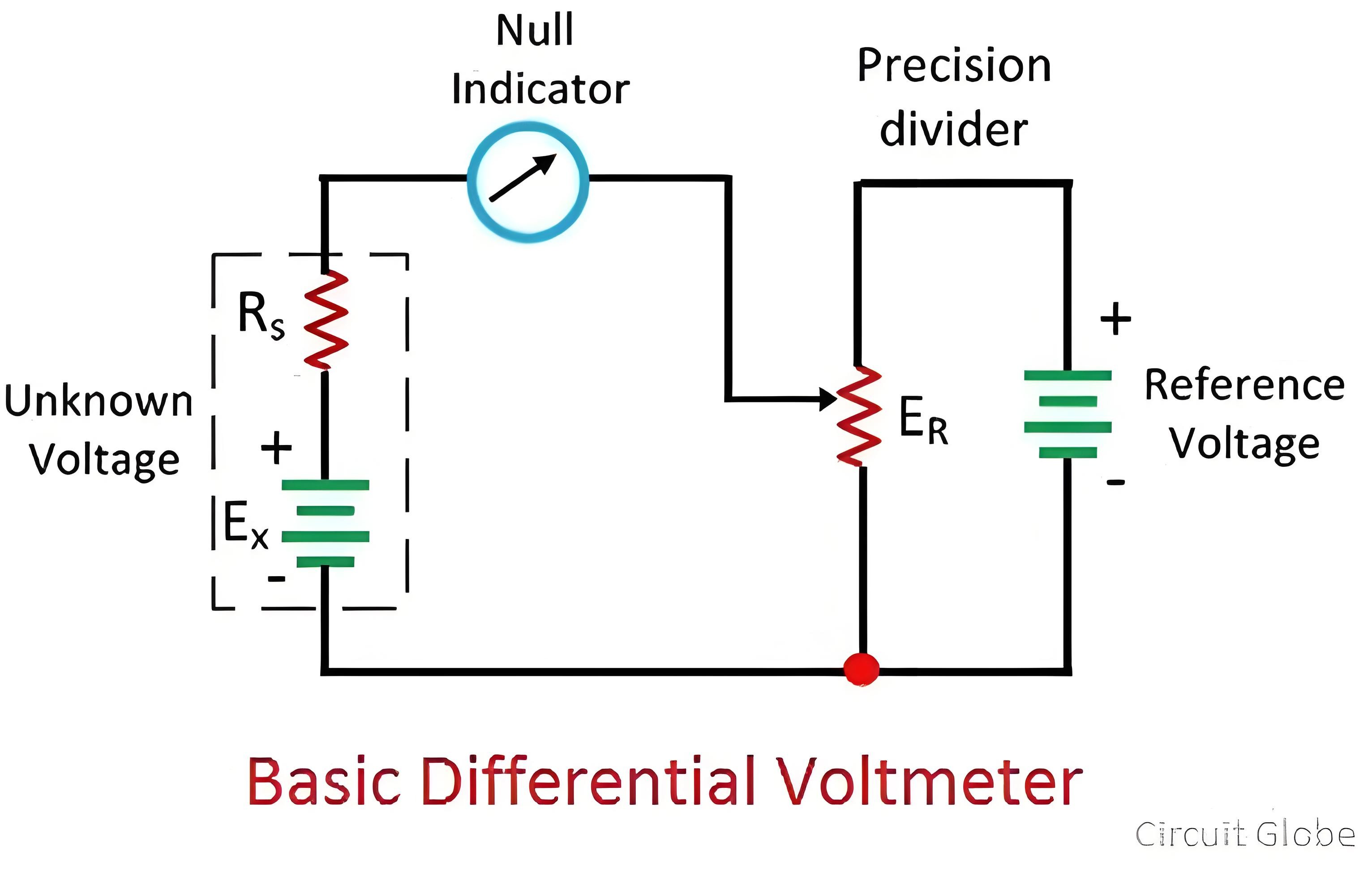
When the meter shows zero deflection, it indicates that the magnitudes of both the known and the unknown voltage sources are equal. At this time of null deflection, neither the known nor the unknown source sends current to the meter, and the voltmeter presents high impedance to the measured source.
The null meter merely indicates the residual difference between the known and the unknown voltage sources. To accurately determine the difference between the sources, a more sensitive meter is employed.
A low - voltage DC standard source or a low - voltage Zener - controlled precision supply is utilized as the reference voltage. High - voltage supplies are used for measuring high voltages.
Types of Differential Voltmeter
There are two types of differential voltmeters:
AC Differential Voltmeter
DC Differential Voltmeter
AC Differential Voltmeter
The AC differential voltmeter is an enhanced version of DC instruments. The unknown AC voltage source is applied to a rectifier, which converts the AC voltage into a DC voltage of equivalent magnitude. The resulting DC voltage is then fed to a potentiometer for comparison with the known voltage source. The block diagram of the AC differential voltmeter is shown below.
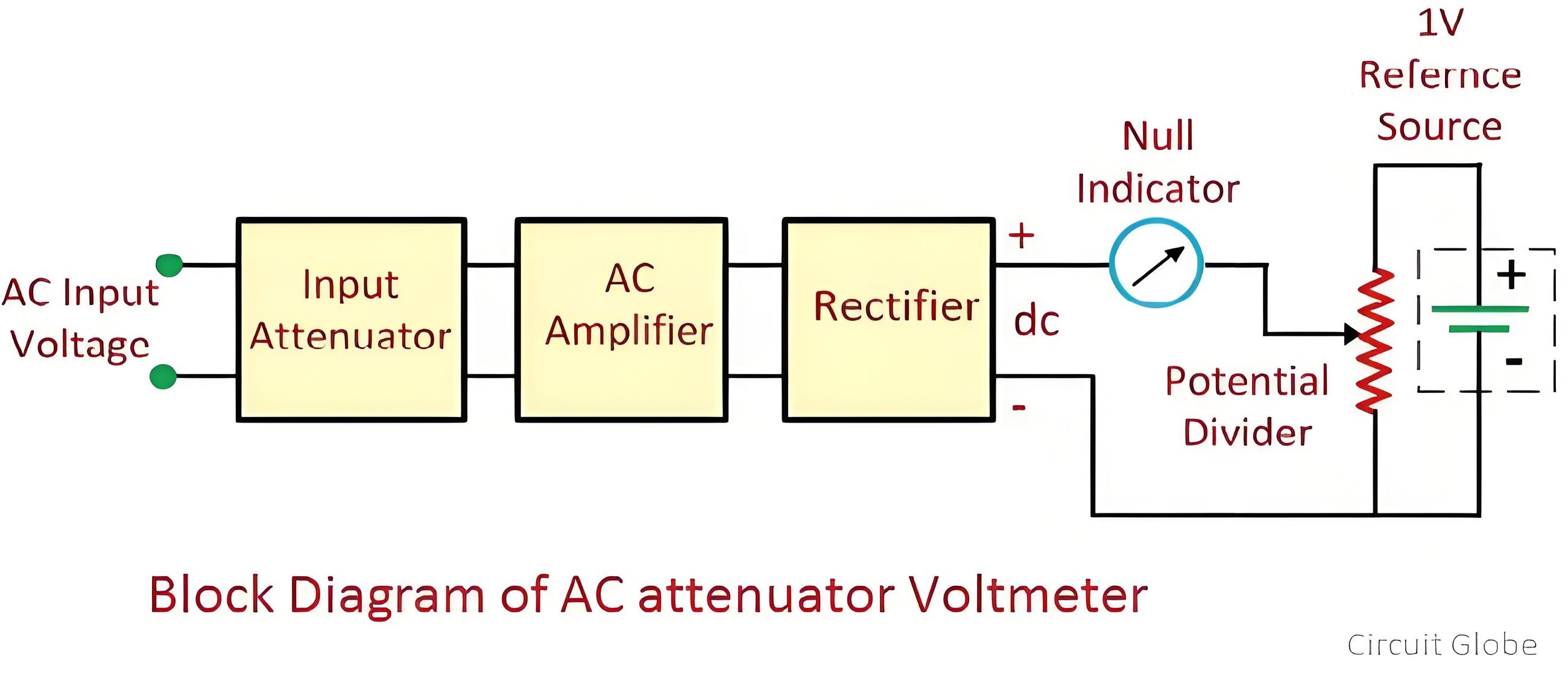
The rectified AC voltage is compared with the standard DC voltage. When their magnitudes are equal, the meter shows null deflection. In this way, the value of the unknown voltage is determined.
DC Differential Voltmeter
The unknown DC source serves as the input to the amplifier section. A fraction of the output voltage is fed back to the input voltage by means of a divider network. Another part of the voltage divider provides a fractional input to the meter amplifier.
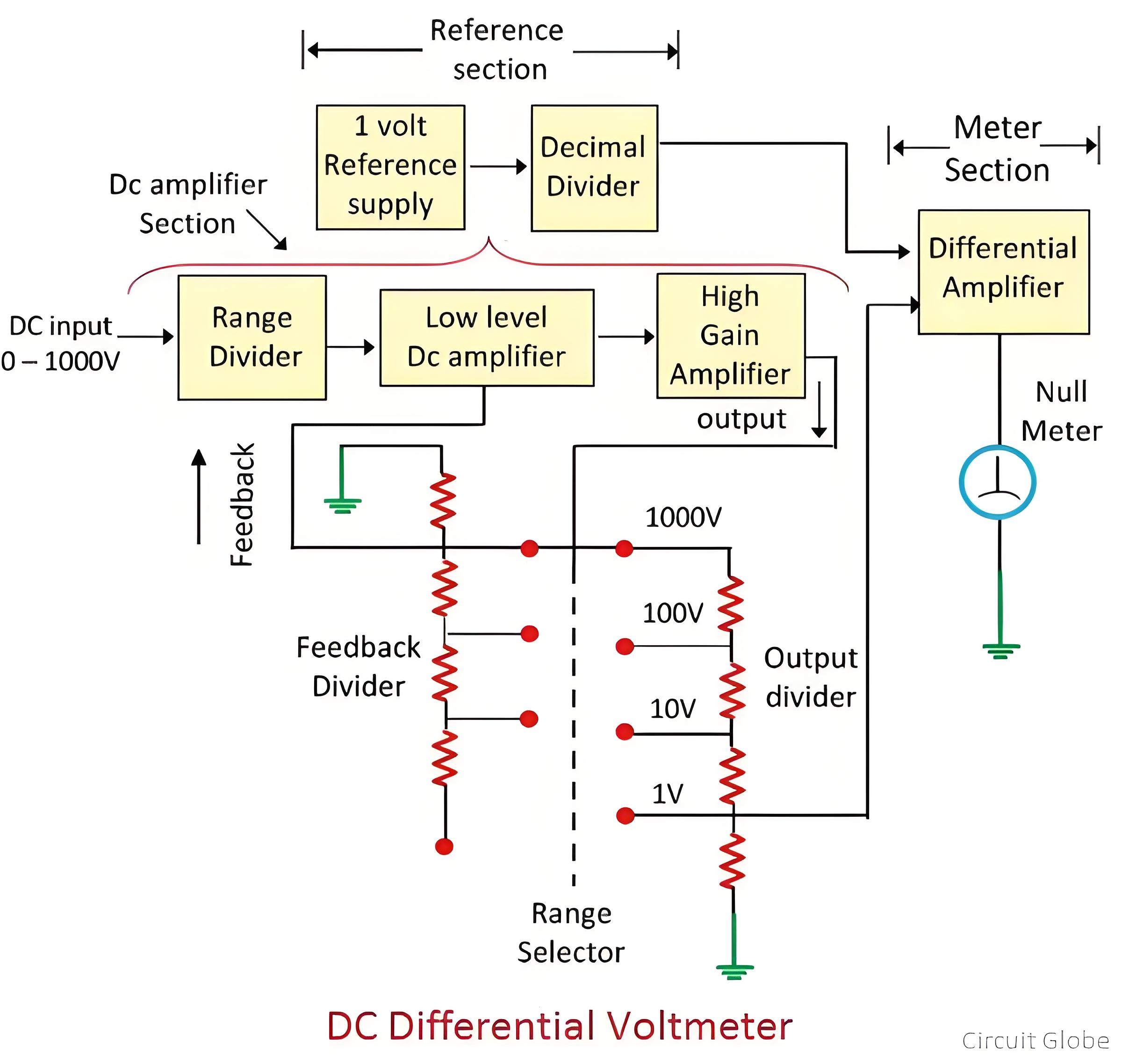
The meter is designed to measure the difference between the feedback voltage and the reference voltage. When the magnitudes of both the unknown voltage and the reference voltage are zero, the null meter indicates null deflection.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













