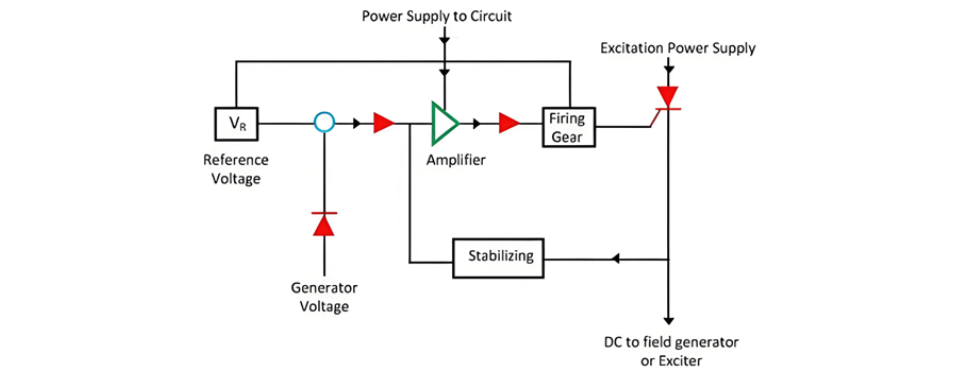
What is Static Voltage Regulator?
Types of Static Voltage RegulatorThe static voltage regulator is superior to electromechanical regulators in respect of the accuracy of control, response, reliability and maintenance. The static voltage regulator is mainly classified into two types. They are;Servo Type Voltage RegulatorMagnetic Amplifier RegulatorThe types of static voltage regulator are described below in details;Servo Type Voltage RegulatorThe main feature of the servo type voltage regulator is the use of the amplidyne. The am
Edwiin
05/21/2025

What is Arc Extinction Circuit Breaker?
When the current-carrying contacts of a circuit breaker separate, an arc forms and persists briefly after contact separation. This arc is hazardous due to the heat energy it generates, which can produce explosive forces.A circuit breaker must extinguish the arc without damaging equipment or endangering personnel. The arc significantly influences the breaker’s performance. Interrupting aDC arcis inherently more challenging than anAC arc. In an AC arc, the current naturally reaches zero duri
Edwiin
05/20/2025

Air Break Circuit Breaker
In an air break circuit breaker, the arc is initiated and extinguished in substantially static air as the arc moves. These breakers are used for low voltages, generally up to 15 kV, with rupturing capacities of 500 MVA. As an arc-quenching medium, air circuit breakers offer several advantages over oil, including:Elimination of risks and maintenance associated with oil use.Absence of mechanical stress caused by gas pressure and oil movement.Elimination of costs from regular oil replacement due to
Edwiin
05/20/2025
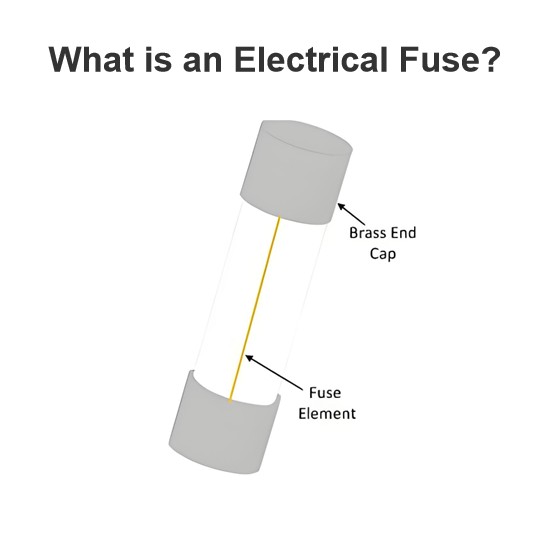
What is an Electrical Fuse?
A fuse is a device employed in electrical circuits to protect electrical equipment against overloads and short circuits. It is the simplest and most cost-effective component for interrupting an electrical circuit when exposed to short-circuit currents or excessive overloads.Fuses are used for overload or short-circuit protection in high-voltage systems of up to 66 kV and low-voltage systems of up to 400 V. In certain applications, their use is limited to scenarios where their performance charact
Edwiin
05/19/2025