Definition
A hygrometer is used to measure the humidity in the surrounding environment, where "humidity" refers to the amount of water vapor in a gas. Hygrometers operate on the principle that the physical properties of materials change in response to humidity, enabling measurement.
Humidity is classified into two types:
- Absolute Humidity: Represents the amount of water vapor per unit volume of air.
- Relative Humidity: The ratio of the actual water vapor pressure to the maximum water vapor pressure achievable by a substance at a specific temperature, which depends on temperature.
Classifications of Hygrometer
Hygrometers are classified by the materials used for humidity measurement, including:
Resistive Hygrometer
A resistive hygrometer features a conducting film made of materials like lithium chloride or carbon, positioned between metal electrodes. The resistance of this film changes with variations in the humidity of the surrounding air.
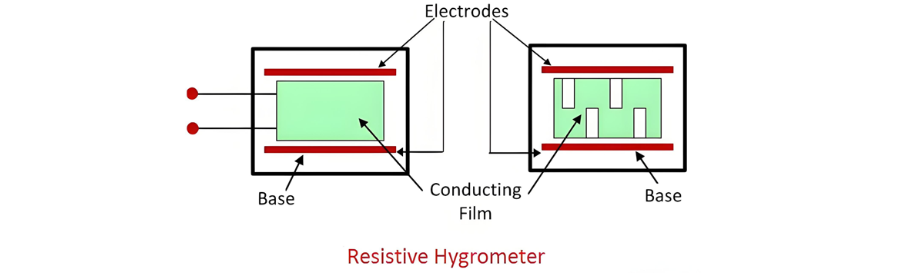
The amount of moisture absorbed by lithium chloride depends on relative humidity. Higher relative humidity causes lithium chloride to absorb more moisture, reducing its resistance.
The change in resistance is measured by applying alternating current (AC) to a bridge circuit. Direct current (DC) is avoided, as it can degrade the lithium chloride layer. Obstructed current flow indicates the resistance value, which correlates to relative humidity.
Capacitive Hygrometer
A capacitive hygrometer measures surrounding humidity via changes in a capacitor’s capacitance, offering high accuracy. It consists of hygroscopic material (which rapidly absorbs water) sandwiched between metal electrodes. Water absorption by the material alters the capacitor’s capacitance, which is detected by an electronic circuit.
Microwave Refractometer
A microwave refractometer measures the refractive index of moist air as humidity changes. The refractive index—the ratio of light velocity in one medium to another—is determined by measuring the dielectric constant (using a capacitor) or frequency shifts in humid air.
Aluminium Oxide Hygrometer
This hygrometer uses anodized aluminium coated with aluminium oxide. Humidity alters the dielectric constant and resistance of the aluminium. It employs aluminium as one electrode and a gold layer as the second electrode.
The second electrode is porous to absorb air-vapour mixtures. Humidity induces changes in the capacitance and resistance of the material, altering its impedance. This impedance is measured using a bridge circuit, making this hygrometer a key component in electronic systems.
Crystal Hygrometer
The figure below illustrates a crystal hygrometer utilizing quartz.
In a crystal hygrometer, a hygroscopic crystal or a crystal coated with hygroscopic material is used. When the crystal absorbs water droplets, its mass changes. The change in mass is proportional to the total water absorbed by the crystal.