Definition
A photoelectric transducer is a semiconductor device that converts light energy into electrical energy. It employs a photosensitive element that emits electrons when struck by light, altering the element’s electrical properties and inducing a current proportional to the intensity of the absorbed light.The schematic below illustrates the structure of the semiconductor material.
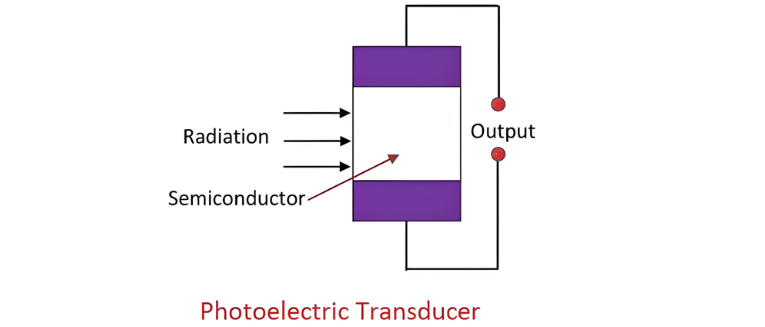
A photoelectric transducer absorbs light radiation incident on its semiconductor material. This absorption energizes the material’s electrons, causing them to move. The electron mobility produces one of three effects:
- A change in the material’s resistance.
- A change in the semiconductor’s output current.
- A change in the semiconductor’s output voltage.
Classification of Photoelectric Transducers
Photoelectric transducers are classified as follows:
Photoemissive Cell
A photoemissive cell converts photons into electrical energy. It contains an anode rod and a cathode plate, both coated with a photoemissive material such as caesium antimony.
When light radiation strikes the cathode plate, electrons begin to flow from the cathode to the anode. Both the anode and cathode are sealed within a closed, opaque evacuated tube. When light radiation reaches the sealed tube, electrons are emitted from the cathode and move toward the anode.
The anode is maintained at a positive potential, causing a photoelectric current to flow through it. The magnitude of this current is directly proportional to the intensity of the light passing through the tube.
Photoconductive Cell
A photoconductive cell converts light energy into electric current. It utilizes semiconductor materials such as cadmium selenide, germanium (Ge), or selenium (Se) as the photosensing element.
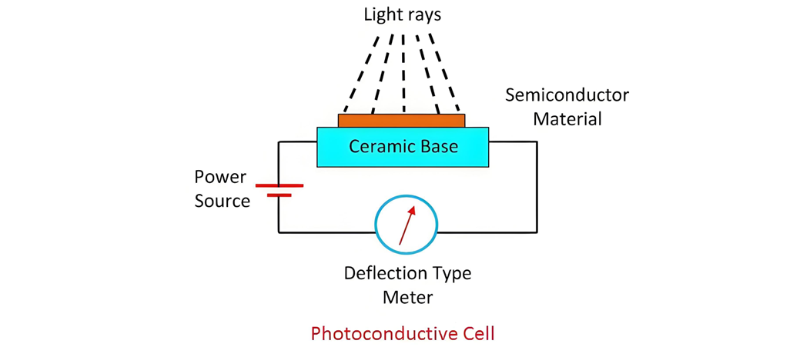
When a light beam strikes the semiconductor material, its conductivity increases, and the material acts like a closed switch. Current then flows through the material, deflecting the pointer of a meter.
Photovoltaic Cell
A photovoltaic cell is a type of active transducer. Current begins to flow in the photovoltaic cell when a load is connected to it. Silicon and selenium are commonly used as semiconductor materials. When the semiconductor material absorbs light (not heat), its free electrons start to move—a phenomenon known as the photovoltaic effect.
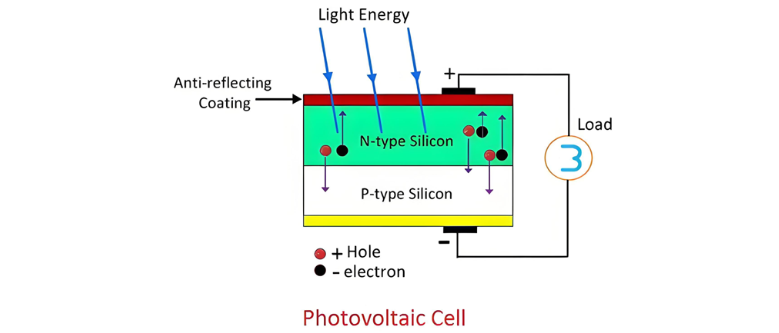
The movement of electrons generates a current in the cell, known as the photoelectric current.
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into current. When a photodiode absorbs light energy, the electrons in its semiconductor material begin to move. The photodiode has a very short response time and is designed to operate under reverse bias.
Phototransistor
A phototransistor is a device that converts light energy into electrical energy, generating both current and voltage.
Photovoltaic Cell
A photovoltaic cell is a bipolar device composed of semiconductor material enclosed in a transparent container, allowing light to reach the photosensitive element easily. When the element absorbs light, a current begins to flow from the base to the emitter of the device, which is then converted into voltage.

