| Brand | ROCKWILL |
| Model NO. | DS4 40.5kV 126kV 145kV 252kV High voltage disconnect switch |
| Rated voltage | 252kV |
| Rated normal current | 2000A |
| Series | DS4 |
Description:
DS4 series disconnector adopts double column horizontal rotation structure, which is composed of three unipolar and operating mechanism. Each monopole consists of a base, a post insulator, and a conducting part. A rotating pillar insulator is installed at both ends of the base, and the contact arm and contact arm of the main electrical part are respectively fixed on the top of the pillar insulator. The operating mechanism drives one end of the pillar insulator to rotate, and drives the other end of the pillar insulator to reverse rotate 90° through the cross connecting rod, so that the conductive knife can turn on the horizontal plane to realize the isolation switch opening and closing. The opening state forms a horizontal insulation fracture.
Main Features:
The conductive arm is made of rectangular aluminum alloy tube or aluminum alloy plate, high strength, light weight, large heat dissipation area, good anti-corrosion performance.
The contact part of the conductive arm adopts external pressure plate spring structure. The plate spring is made of alloy material with good elasticity, which can keep the contact pressure stable for a long time and overcome the drawbacks of the spring internal pull structure.
Technical parameter
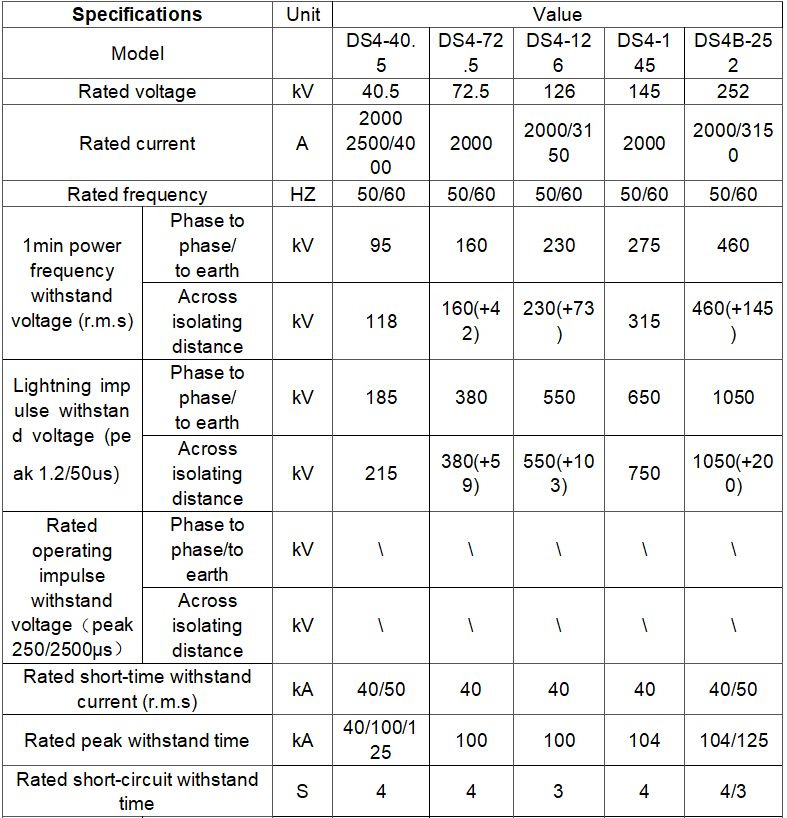
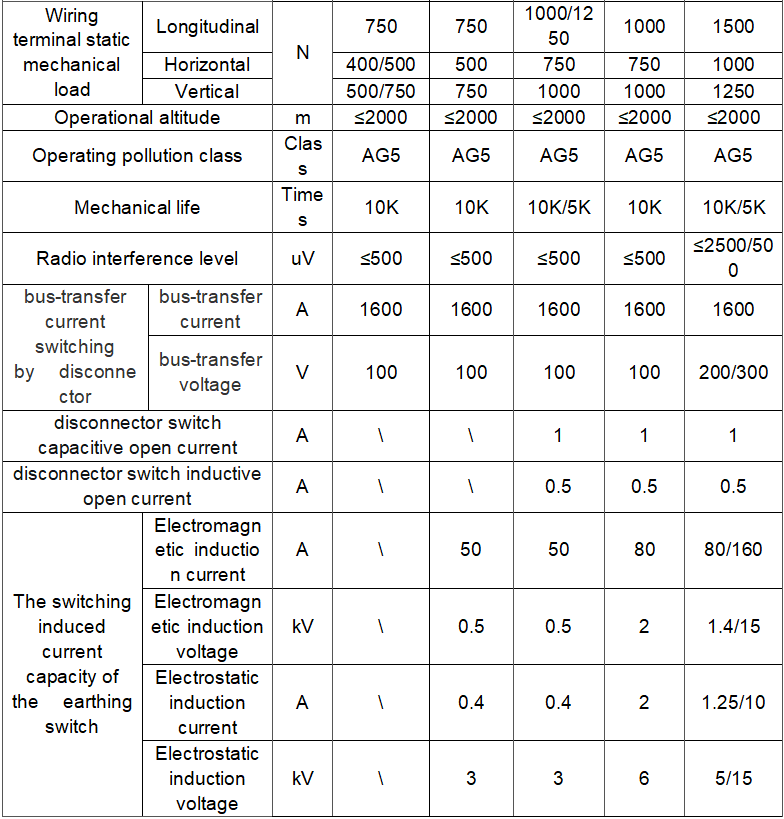
What are the structural characteristics of the disconnector?
Contact System:
Description: The contact system is a critical part of the isolator switch, consisting of moving contacts and stationary contacts. The moving contact is typically connected to the operating handle via a transmission mechanism and can move to engage or disengage from the stationary contact under the influence of the operating force.
Surface Treatment: To ensure good contact performance, the contact surfaces are often specially treated, such as silver plating. This reduces contact resistance and minimizes heat generation.
Shape Design: The shape of the contacts is also important. Common types include knife-blade contacts and finger contacts, which provide a larger contact area to ensure safe and stable current flow.
Description: The insulation part ensures that there is sufficient insulation between different potential sections of the isolator switch. It is mainly composed of insulators, which are typically made of ceramic, glass, or composite materials.
Ceramic Insulators: Ceramic insulators have excellent insulation properties, mechanical strength, and weather resistance, making them suitable for various harsh environmental conditions.
Glass Insulators: Glass insulators have good self-cleaning properties, reducing the impact of dust and dirt on insulation performance.
Composite Insulators: Composite insulators are lightweight and have excellent pollution flashover resistance, making them advantageous in special application scenarios.
Description: The transmission mechanism is used to transfer the operating force from the operating handle to the moving contact, enabling the opening and closing actions of the contacts. It can be a manual linkage mechanism or an electric operating mechanism.
Manual Linkage Mechanism: This type of mechanism is simple in structure and highly reliable. It converts the rotational motion of the operating handle into linear or rotational motion of the moving contact through a series of linkages and shafts.
Electric Operating Mechanism: Suitable for applications requiring remote control or frequent operation, this mechanism uses a motor, reduction gear, and transmission components to achieve automated operation of the isolator switch.
Description: The base and support are the supporting structures of the isolator switch, used to fix the contact system, insulation part, and transmission mechanism. The base is usually made of metal and has sufficient mechanical strength and stability to bear the weight of the isolator switch and various forces generated during operation.
Design Considerations: The support is designed based on the installation method and application scenario of the isolator switch. For example, the support structure of indoor isolator switches differs from that of outdoor isolator switches. Outdoor isolator switches require supports that consider factors such as wind resistance, rain protection, and corrosion resistance.






