What is a Resistance Box?
Resistance Box: Definition, Types, and Operation
Definition
A resistance box is a device that houses resistors of various values, primarily used for estimating and comparing electrical resistance. Renowned for its high accuracy, its main function is to regulate the precise amount of current flowing through an electrical circuit.
Advantages
One of the key benefits of a resistance box is its ability to provide variable resistances in a single, centralized unit. In scenarios where a circuit demands variable resistance, there's no need to physically replace individual resistors. Instead, the circuit can be directly connected to the resistance box, and by simply adjusting the rotary switches, different resistance values can be easily obtained.
Types of Resistance Boxes
Resistance boxes are classified into three main types:
High Resistance Box: This type typically offers resistance values ranging from 1Ω to 5000Ω or even higher.
Low Resistance Box: The resistance values in a low resistance box generally fall within the range of 1Ω to 500Ω.
Fractional Resistance Box: As the name implies, this box provides resistance values in fractional form, with a typical range spanning from 0.1Ω to 50Ω.
The construction of resistance boxes is straightforward and cost - effective, and they come in a variety of designs. They are indispensable tools for testing and designing circuits within laboratory settings.
Simple Resistance Box
Construction
A simple resistance box features two copper terminals, which serve as connection points for the positive and negative ends of an electrical circuit. The box's cover, which houses the terminals and knobs, is crafted from ebonite, a durable and insulating material. The knobs are used to add or remove resistance from the circuit.
On the reverse side of the ebonite sheet, resistors of different values are connected in series. To incorporate a specific resistance into the circuit, the corresponding knob must be removed. When all knobs are placed in the air gap position, the current flows through the copper studs, effectively bypassing all resistors and creating a short - circuit condition with zero resistance added to the circuit.
Usage Guidelines
Power Dissipation Consideration: The resistance values in a box are often set relatively high to minimize power dissipation in the connecting circuit. This helps in reducing energy losses and maintaining the integrity of the circuit components.
Initial Setup: Before connecting the resistance box to a circuit, it is crucial to set the resistance to its minimum value. This precautionary step ensures that minimal power is dissipated in the circuit during the initial connection, preventing potential damage to sensitive components.
Resistance Relationship: The resistance of the box should be equal to or greater than the resistance of the circuit it is connected to, to ensure proper control and regulation of the current flow.
Connection Method: Resistance boxes are always connected to circuits using plug connectors, which provide a secure and reliable electrical connection.
Decade Resistance Box
Construction and Operation
In a decade resistance box, resistors are securely fixed inside the enclosure. These resistors are meticulously arranged to enable step - wise variation of the resistance value. The box is equipped with a rotary selector switch, which is the primary means of obtaining variable resistances. While key plugs can also be used for selecting resistances, rotary switches are preferred due to their ease of use and precision, making them the standard choice in most resistance boxes.
Example of a Normal Decade Resistance Box
The following illustrates the typical arrangement of rotary switches in a standard decade resistance box:
Switch One: Offers a resistance range from 1 to 10 ohms.
Switch Two: Covers a range of 10 to 100 ohms.
Switch Three: Has a range of 100 to 1000 ohms.
Switch Four: Handles resistance values of 100 ohms and above.
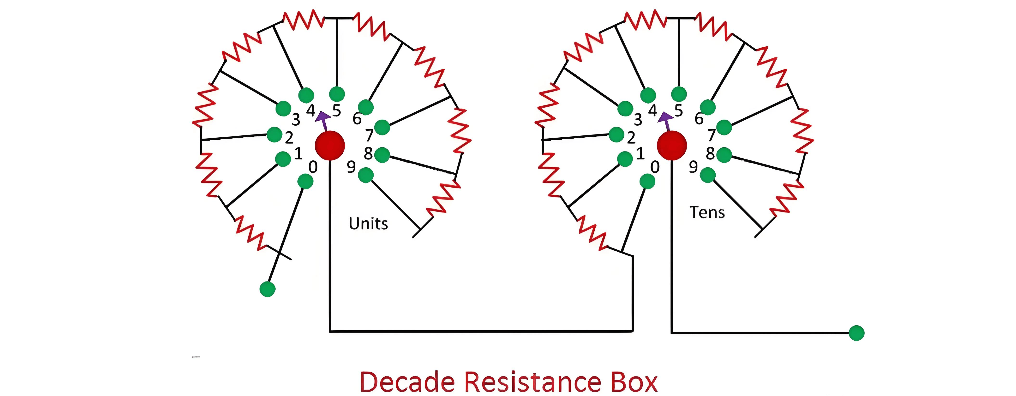
As depicted in the figure above, a resistance box is equipped with multiple rotary switches. Each of these selector switches is designed to provide resistance values that can vary within the range of a few ohms, enabling precise adjustment of the overall resistance offered by the box.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













