Different Layouts for Substation
A substation is a crucial component of an electrical supply system. It serves to transmit high - voltage electricity from generating substations to local distribution networks. During the journey from power generation to distribution, the voltage often undergoes changes across multiple substations. Below, the various types of substation layouts are explained in detail.
Typical Radial Substation
As depicted in the figure below, a radial substation has a single power source for supplying the load. This supply system is considered unreliable. In the event that the source fails or a fault occurs in the line, it will lead to a complete blackout. Such a type of substation is often utilized in the distribution system, especially in rural areas. This is mainly due to the relatively lower significance of power supply reliability in these regions compared to more critical urban or industrial areas.
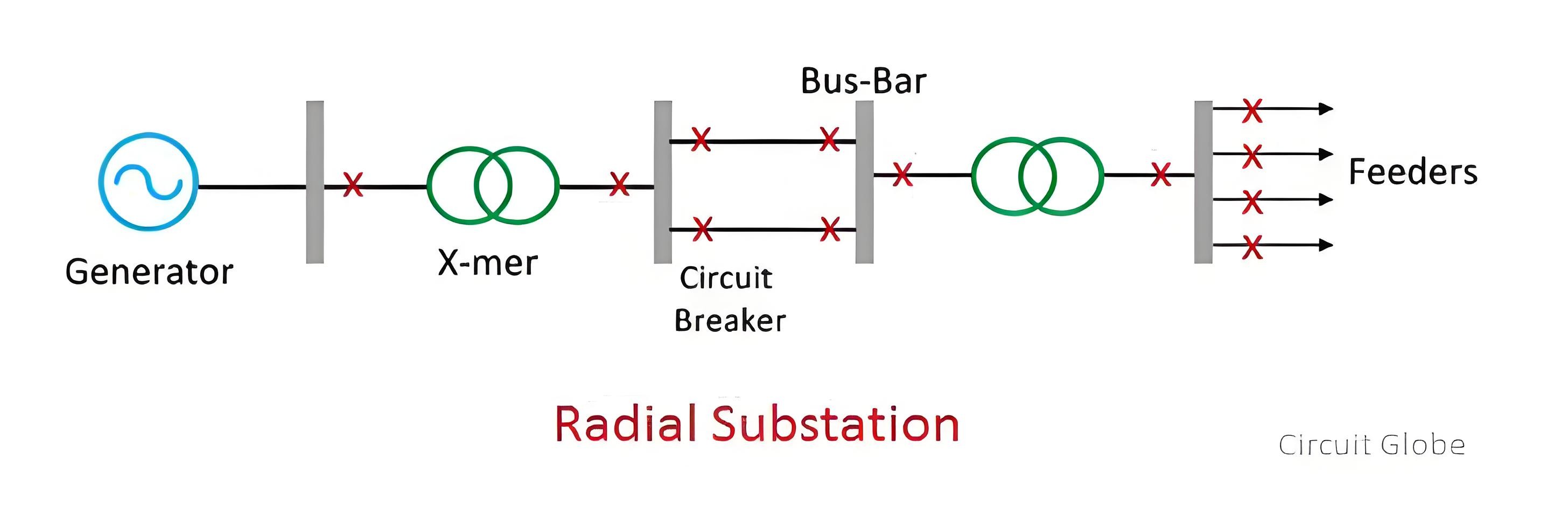
Tapped - Substation
This power supply arrangement is similarly unreliable and insecure. A total supply failure will occur if either the source malfunctions or the line develops a fault.
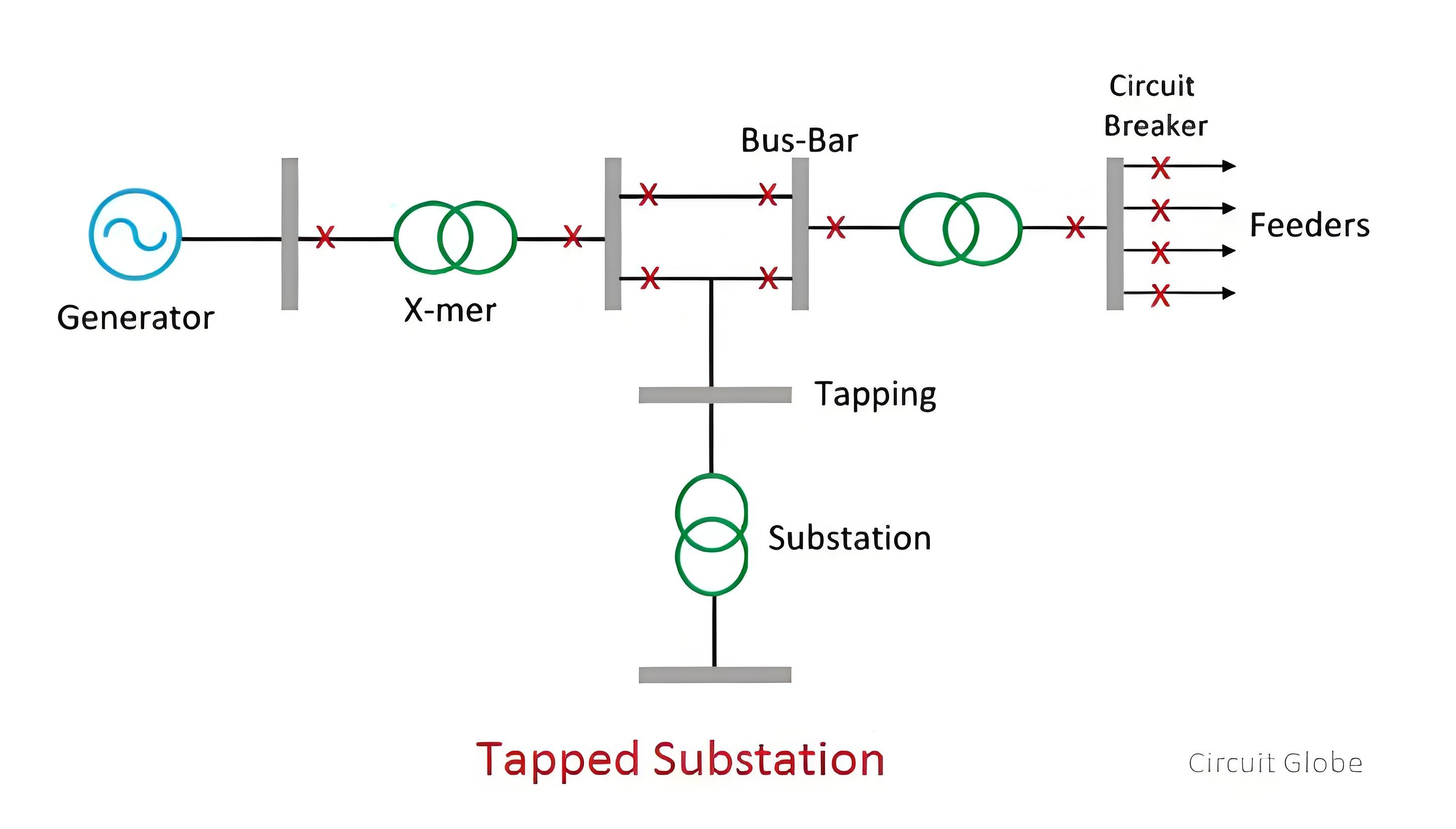
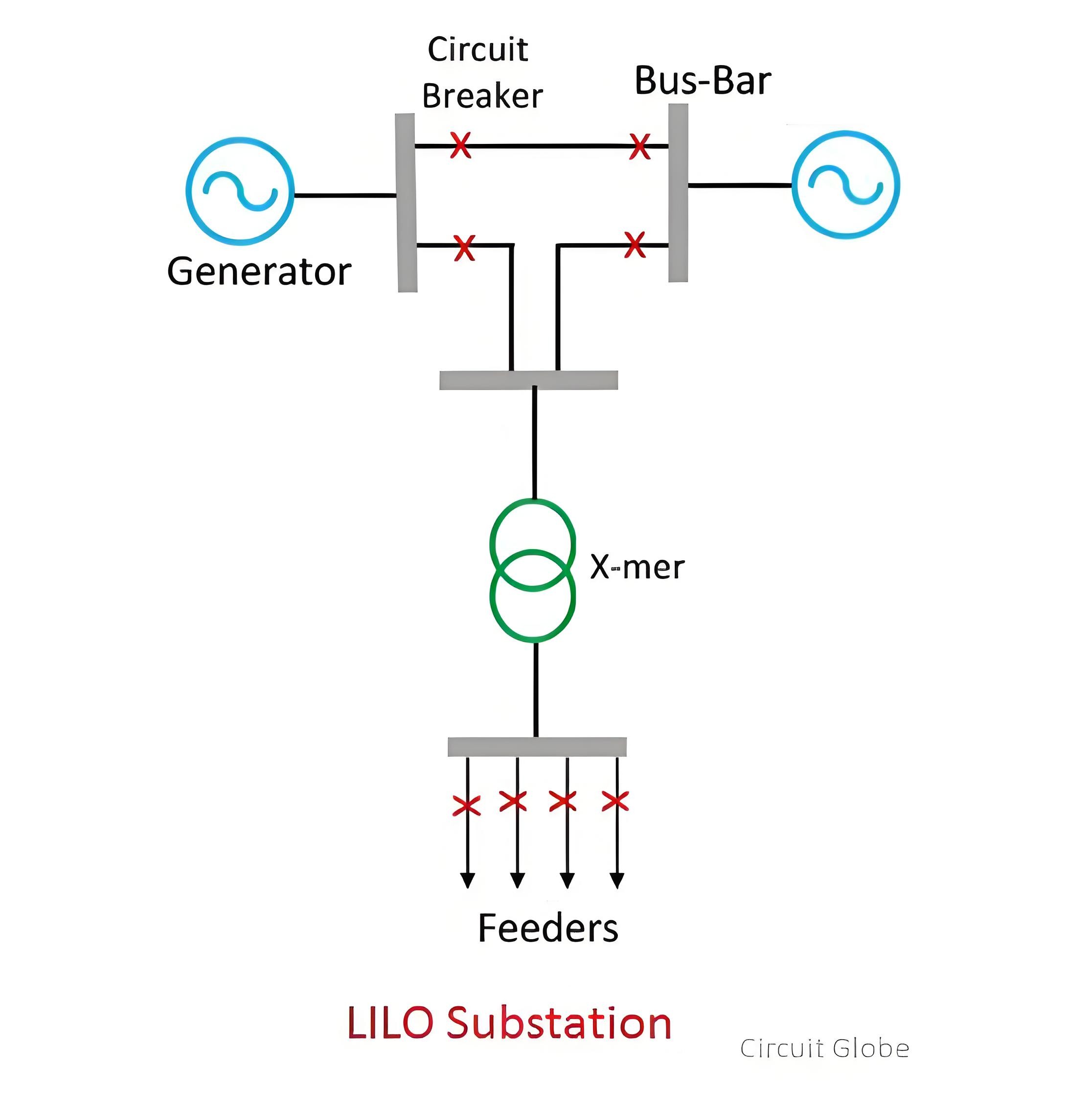
LILo (Line In Line Out) Substation
As illustrated below, in an LILo substation, a long distribution line enters the newly constructed substation and then exits it. This setup is somewhat costly due to the requirement for an additional layout configuration. However, it offers enhanced security in power supply, as it provides alternative paths for electricity flow compared to simpler substation types, reducing the likelihood of total power outages in case of certain faults.
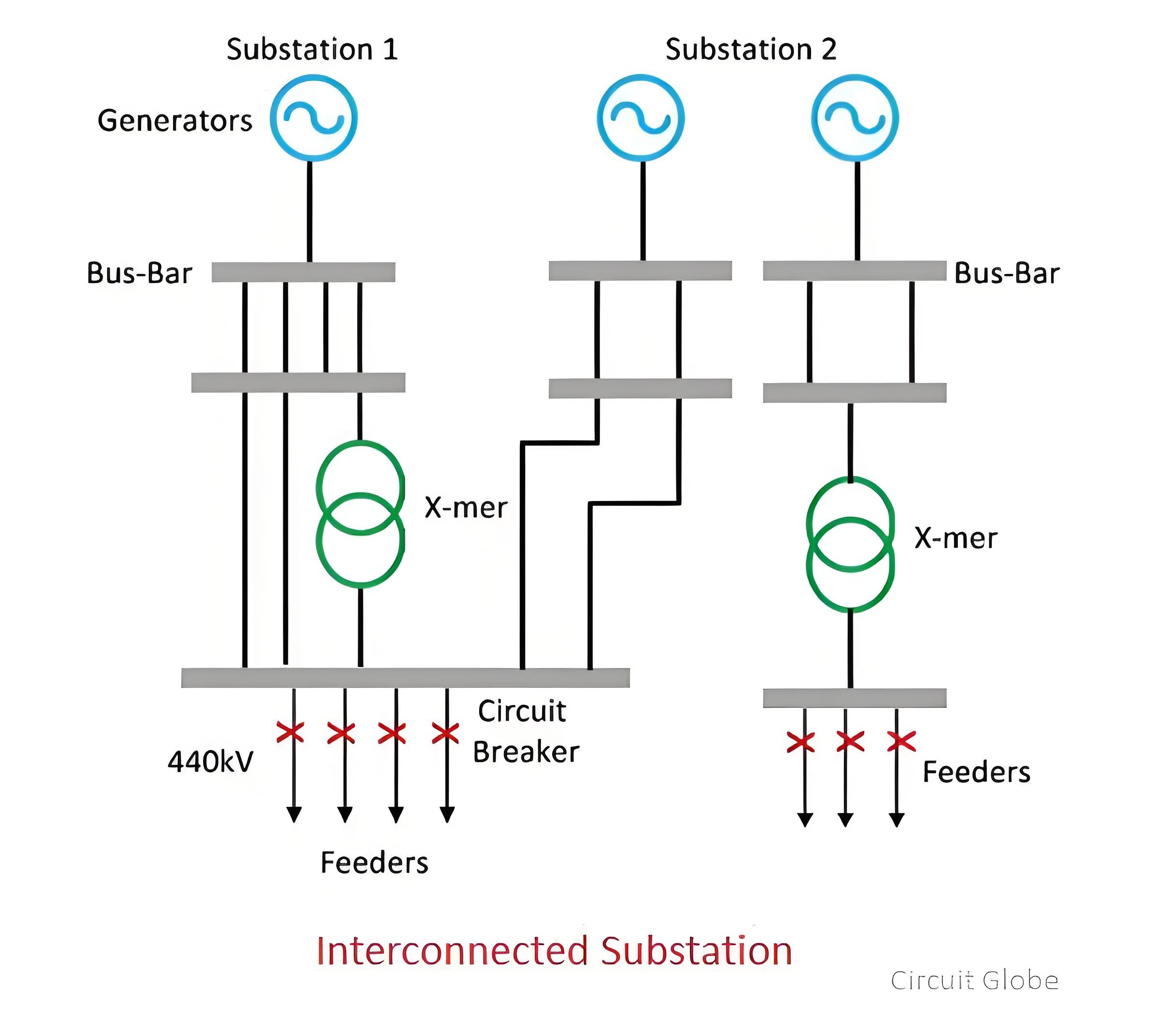
Interconnected Substation
The interconnected substation represents the most favored power supply system. It is highly safe, secure, and reliable. In the event of an outage of a source or a line, the power supply system remains unaffected. This is because numerous alternative paths for power transfer are available within the interconnected network, ensuring continuous electricity supply.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













