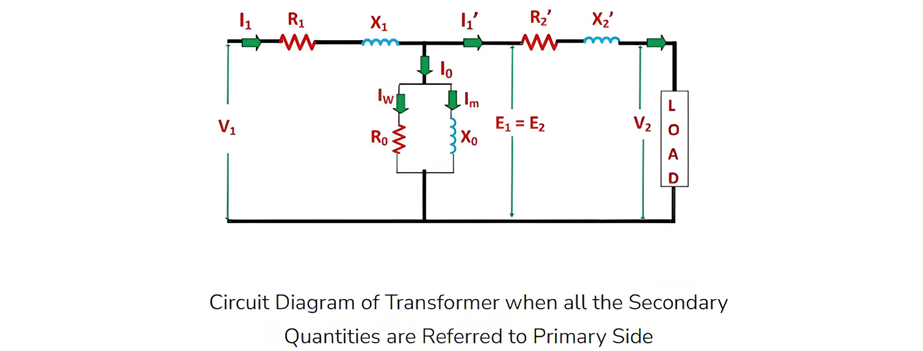
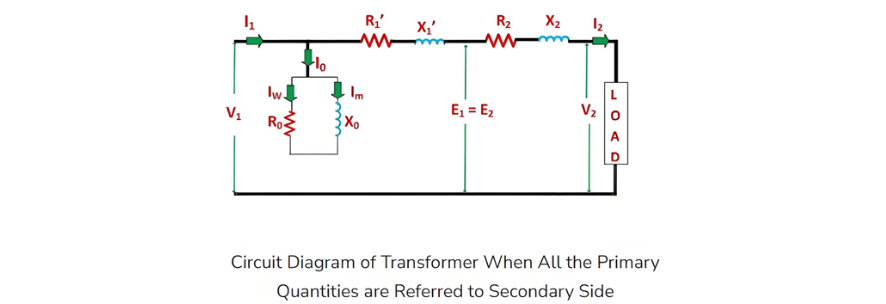
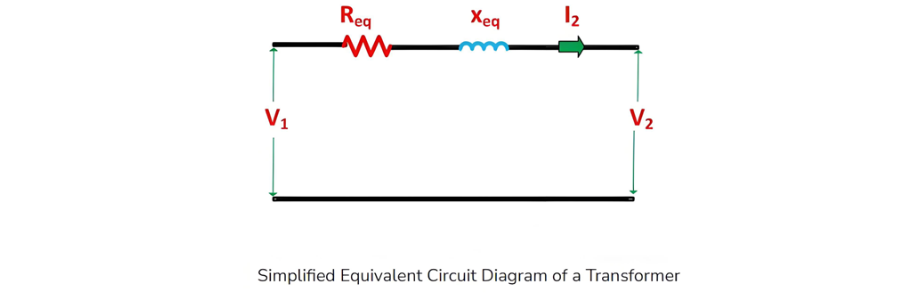
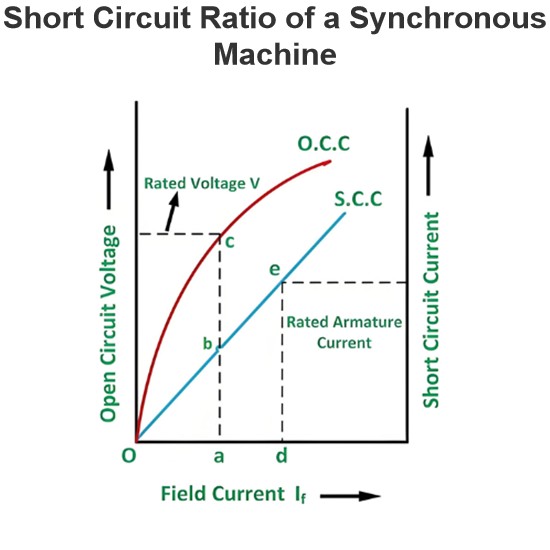
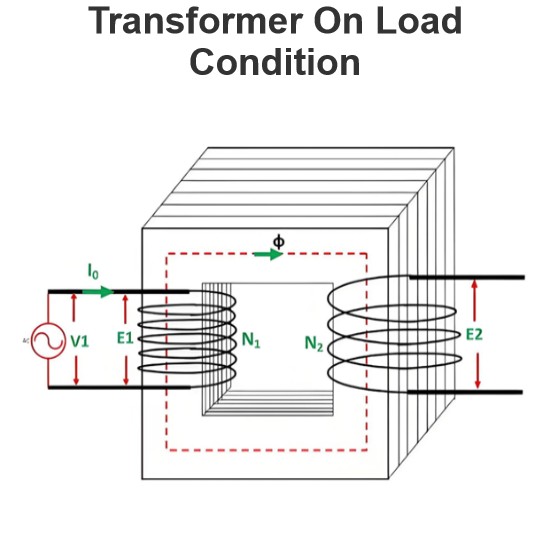
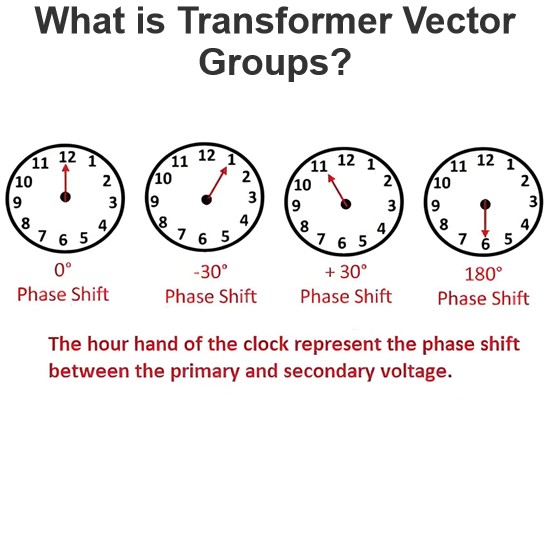
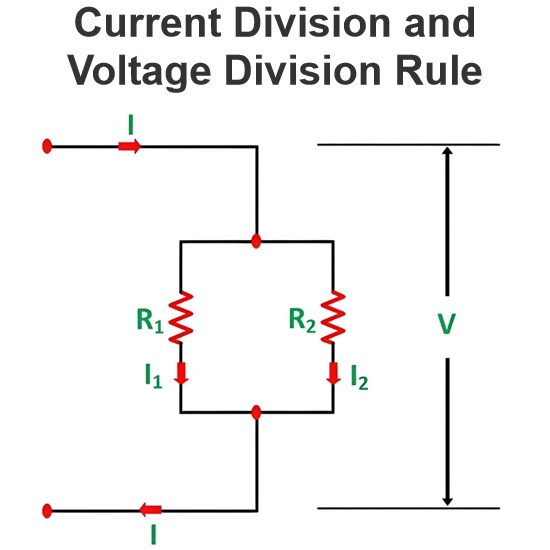
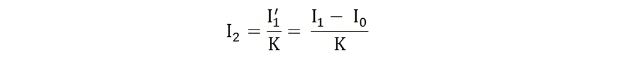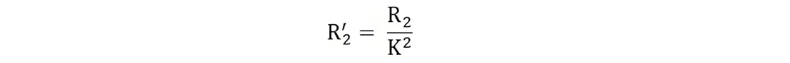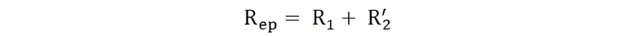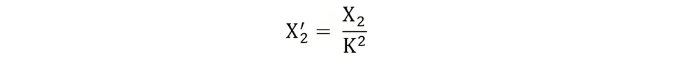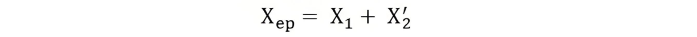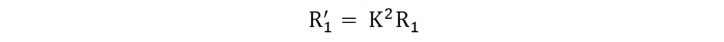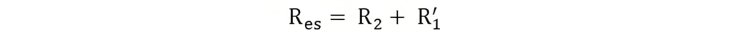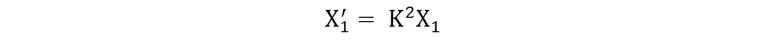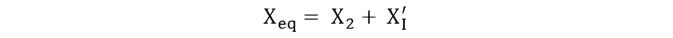Equivalent Circuit of a Transformer
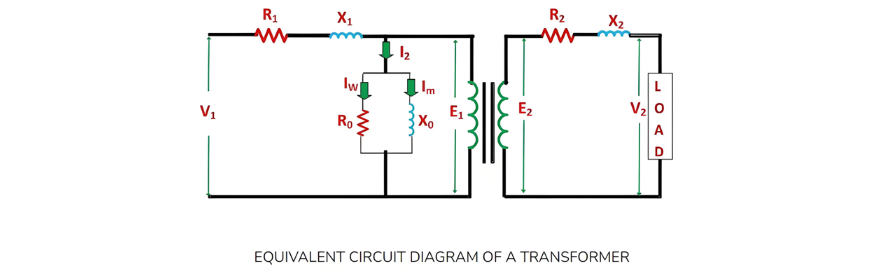
Let the equivalent circuit of a transformer be considered, with a transformation ratio K = E2/E1.The induced electromotive force E1 is equivalent to the primary applied voltage V1 minus the primary voltage drop. This voltage gives rise to the no - load current I0 in the primary winding of the transformer. Since the value of the no - load current is extremely small, it is often neglected in many analyses.Consequently, I1≈I1′. The no - load current I0 can be further decomposed into two components: the magnetizing current Im and the working current Iw.These two components of the no - load current are a result of the current drawn by a non - inductive resistance R0 and a pure reactance X0, across which the voltage is E1 (or equivalently, V1−primary voltage drop).