The rated system - source short - circuit breaking current refers to the maximum system - source short - circuit current that occurs at the moment of contact separation. A generator circuit - breaker is required to be able to interrupt this current under the conditions specified in relevant standards. This particular current is observed in a circuit where the power - frequency recovery voltage aligns with the rated voltage of the generator circuit - breaker, and the transient recovery voltage matches the value defined by the standards.
This rated current is defined by two key parameters: a) Root - Mean - Square (r.m.s.) Value of the Alternating - Current (a.c.) Component Isc: This value represents the effective magnitude of the a.c. part of the short - circuit current and is crucial for determining the thermal stress on the circuit - breaker and other components during a short - circuit event. b) Direct - Current (d.c.) Time Constant of the Rated System - Source Short - Circuit Breaking Current: It characterizes the decay rate of the d.c. component of the short - circuit current, which has implications for the mechanical and electrical forces acting on the circuit - breaker contacts during the breaking process.
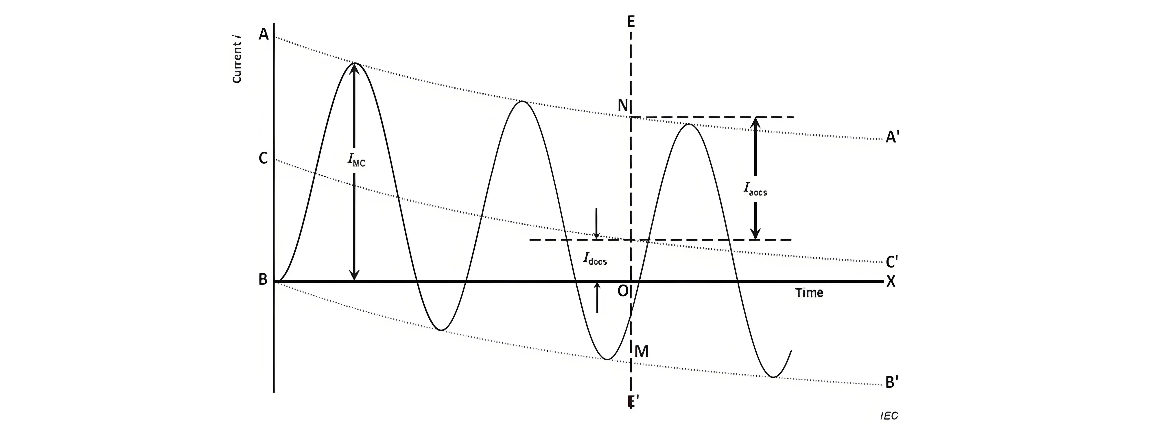
A typical asymmetrical system - source short - circuit current curve is illustrated in the figure. Here's a detailed breakdown of the elements depicted:
- AA’ and BB’: These lines represent the envelope of the current wave, indicating the upper and lower bounds of the current's magnitude over time during the short - circuit event.
- BX: The current zero line marks the points where the current crosses the zero - value axis, which are significant for analyzing the behavior of the circuit - breaker during the interruption process.
- CC’: This is the center line of the current - wave envelope, providing a reference for understanding the overall trend and symmetry of the current waveform.
- EE’: Denotes the instant of contact separation, a critical moment in the operation of the circuit - breaker when it begins to interrupt the short - circuit current.
- Imc: Represents the peak value of the making current, which is the maximum current that the circuit - breaker contacts may experience when closing onto a short - circuit.
- Iaccs: Signifies the peak value of the a.c. component of the current at the instant of contact separation (EE’), highlighting the a.c. stress on the circuit - breaker at this crucial moment.
- Idccs: Indicates the d.c. component of the current at the instant of contact separation (EE’), which contributes to the overall asymmetry of the short - circuit current and affects the breaking performance of the circuit - breaker.
Source: IEC/IEEE 62271 - 37 - 013