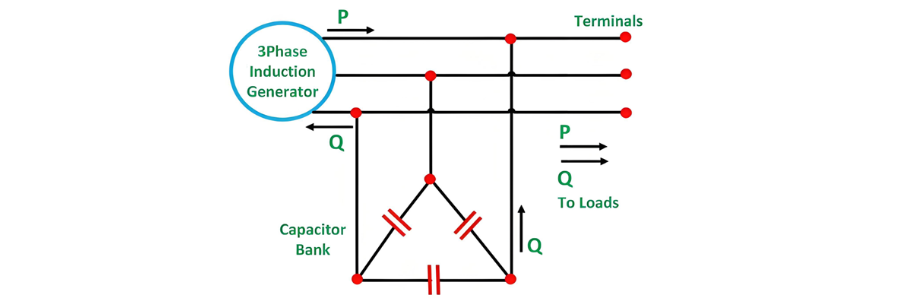
An isolated induction generator refers to an induction machine that is capable of operating as a generator independently, without relying on an external power supply system. As depicted in the following figure, a three - phase delta - connected capacitor bank is connected across the terminals of the machine. This capacitor bank serves to provide the essential excitation for the machine.
The residual flux within the machine serves as the initial excitation source. In cases where residual flux is absent, the machine can be briefly operated as an induction motor to generate the necessary residual flux. A prime mover drives the motor to run slightly above the synchronous speed under no - load conditions. Consequently, a small electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the stator, with its frequency being proportional to the rotor speed.
The voltage across the three - phase capacitor bank induces a leading current in the capacitor bank. This current is nearly equivalent to the lagging current fed back to the generator.
The magnetic flux generated by this current reinforces the initial residual flux, leading to an increase in the total magnetic flux. As a result, the voltage across the machine increases. This rise in voltage prompts an increase in the exciting current, which in turn further elevates the terminal voltage.
At this juncture, the reactive volt - amperes demanded by the generator are equivalent to those supplied by the three - phase delta - connected capacitor bank. The operating frequency hinges on the rotor speed, and any variation in the load has an impact on the rotor's rotational speed. The voltage is predominantly regulated by the capacitive reactance at the operating frequency.
A significant drawback of an isolated induction generator is that when faced with a load having a lagging power factor, the voltage drops precipitously.
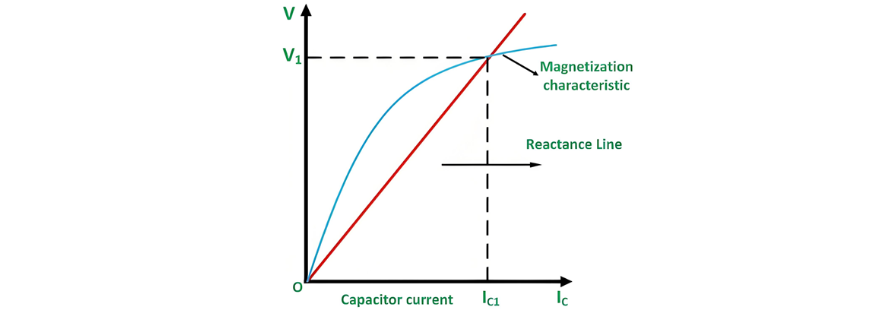
This voltage increase persists until the magnetization characteristic curve of the machine intersects with the voltage - current characteristic curve of the capacitor bank. The following graph illustrates the magnetization curve and the V - IC (Voltage - Capacitor Current) characteristic.