Coil Span Factor (Pitch Factor) Definition and Characteristics
Definition of Pitch Factor (Kₙ)
The coil span factor (also known as the chording factor) Kₙ is defined as the ratio of the induced voltage in a short-pitched coil to that in a full-pitched coil. The distance between the two sides of a coil is termed the coil span, which is characterized by its electrical angle to indicate the degree of short-pitching.
Physical Meaning of Pole Pitch
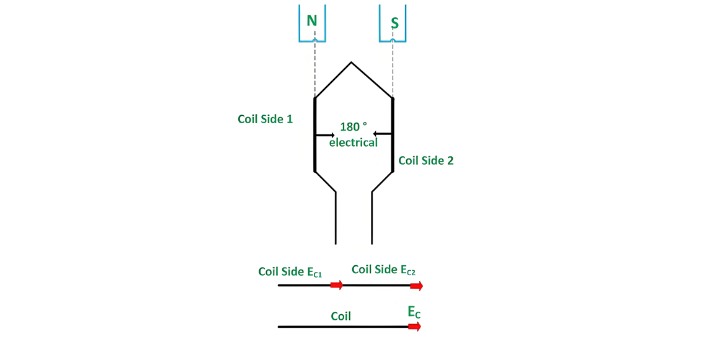
The angular distance between the central lines of adjacent poles is called the pole pitch, which always equals 180 electrical degrees regardless of the number of poles in the machine. A coil with a span of 180 electrical degrees is referred to as a full-pitched coil, as illustrated in the figure below:
Short-Pitched Coil Characteristics
A coil with a span less than 180 electrical degrees is termed a short-pitched coil (or fractional-pitch coil), also known as a chorded coil. The short-pitch coil configuration is illustrated in the figure below:
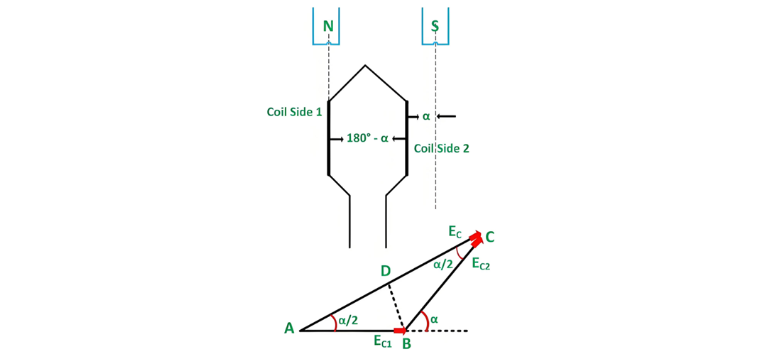
Chorded Winding and Coil Span Calculation
A stator winding employing fractional-pitch coils is referred to as a chorded winding. If the coil span is reduced by an electrical angle α, the effective span becomes (180 – α) electrical degrees.
For a full-pitch coil, the distance between the two coil sides precisely equals the 180° electrical pole pitch, ensuring that voltages induced in each coil side are in phase. Let EC1 and EC2 denote the voltages generated in the coil sides, with EC as the resultant coil voltage. The relationship is expressed by the equation:
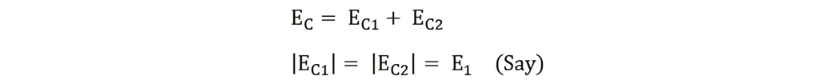
Since EC1 and EC2 are in phase, the resultant coil voltage EC equals the arithmetic sum of the two voltages.
Thus,
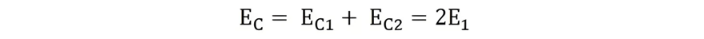
Phasor Analysis of Short-Pitched Coils
When the coil span of a single coil is less than the 180° electrical pole pitch, the voltages induced in each coil side EC1 and EC2 exhibit a phase difference. The resultant coil voltage EC is the phasor sum of EC1 and EC2.
If the coil span is reduced by an electrical angle α, the effective span becomes (180 – α) degrees. Consequently, EC1 and EC2 will be out of phase by α degrees. As shown in the phasor diagram above, the phasor sum EC corresponds to the vector AC.
The coil span factor Kc is expressed as:
- Full-pitched coil: When α = 0°, cos(α/2) = 1, hence Kₙ = 1.
- Short-pitched coil: Kₙ < 1, indicating that short-pitching reduces the amplitude of induced voltage.
Technical Advantages of Short-Pitched Coils (Chorded Windings)
-
Material Cost Optimization:Shortens winding end-turn lengths, reducing conductor material usage and manufacturing costs.
-
Waveform Quality Enhancement:Suppresses harmonic distortion, making the induced EMF closer to a sine wave and improving power quality.