EcoStruxure Power Digital Solutions and Services for Auxiliary Power Systems
What is it?
Auxiliary Power Systems are electrical distribution systems
incorporated in the railway infrastructure to power loads
that require electricity for their operation, such as:
• Interlocks and other signaling equipment
• Track sensors
• Point heaters
• Telecommunications equipment
• Other technical buildingsThey are particularly used in areas where it is not possible to find a regular supply of electricity.
• 25% of the total energy of the railway system is consumed by auxiliary power systems.

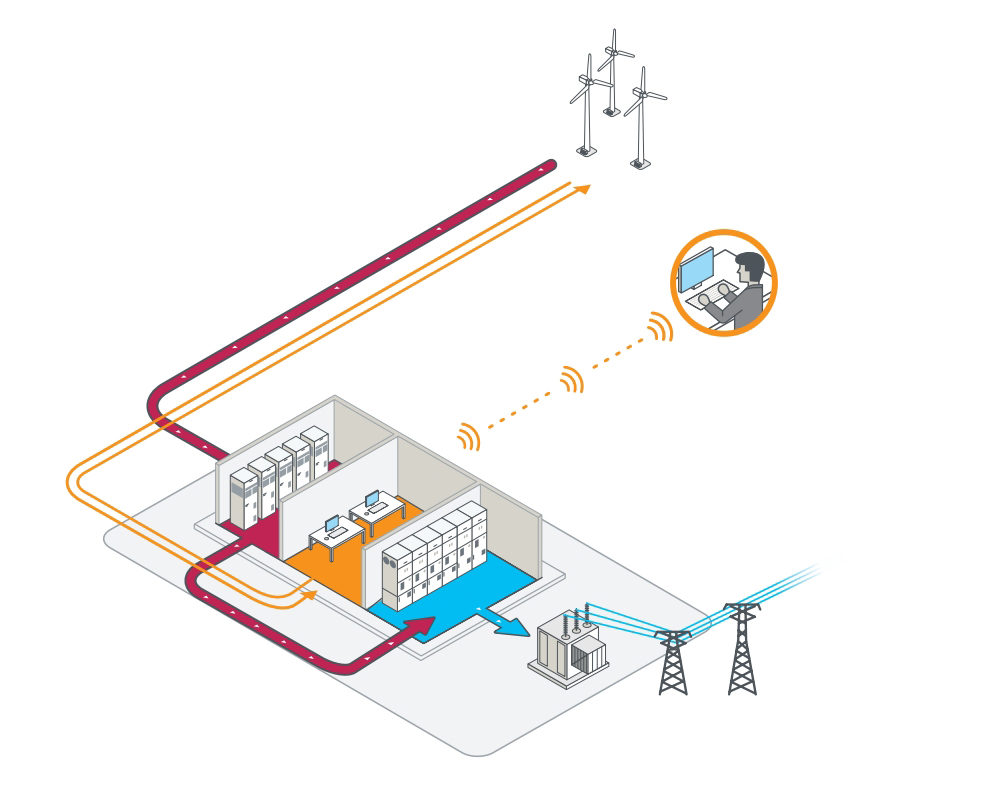
How it works?
To ensure high reliability, auxiliary power systems use
dual-source power distribution loops.
This setup provides redundancy by connecting two
independent power sources, allowing uninterrupted
operation even if one source fails.
Key Benefits:
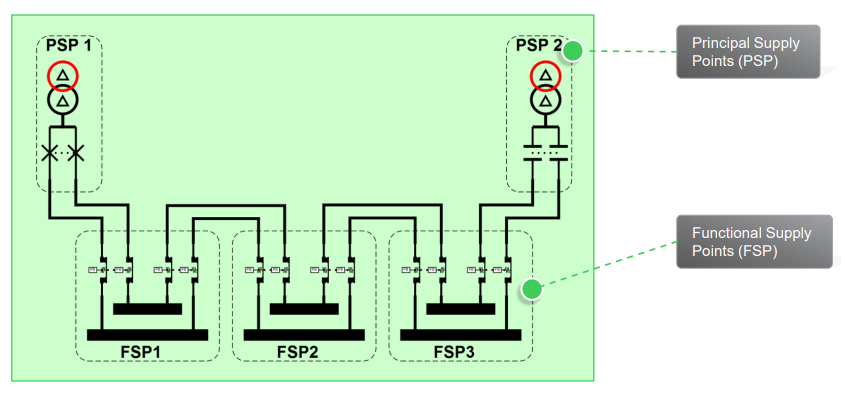
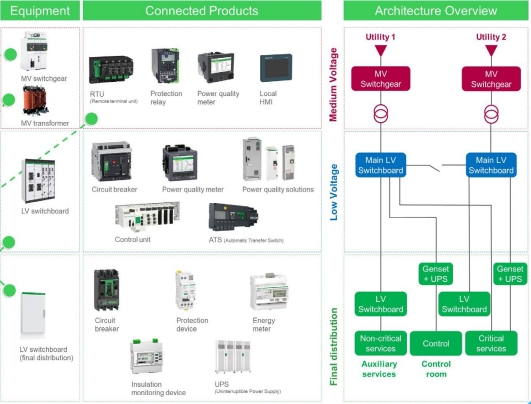
Main components of the electrical architecture solution
Key Components of the Electrical Architecture
Medium Voltage (MV) Switchgear Cabinets
•Three-phase distribution cabinets for power control
and protection.
•Isolate faults and maintain system stability.
Auxiliary Power Transformer (Dry-Type)
•Converts voltage levels to support auxiliary systems
safely.
Control, Protection & Measurement Equipment
•Relays, circuit breakers, and sensors for fault detection.
•Real-time monitoring of voltage, current, and power
quality.
Low Voltage (LV) Distribution Equipment
•Switches, distribution panels, and cooling systems.
•Ensures safe power delivery to end-use applications