Photovoltaic inverter

Peculiarity:
♦ Dual phase inverter.
♦ Up to 9 parallel machines, the output power can reach 45KW.
♦ Three parallel machines can be set up three-phase power supply
♦ Backward compatible with traditional lead batteries, colloidal batteries.
♦ The panel integrates a variety of interfaces, supporting a variety of protocols of the host computer and battery pack.
♦ Integrated MPPT, maximize the press of the remaining power of the photovoltaic panel.
♦ Highly integrated, feature-rich, one machine at most.
♦ PC PLUS-5 Standard 4U rack specifications.
♦ Can be customized adjustment management battery charging and discharging strategy.
♦ Modular design, easy maintenance.
Technical parameter:
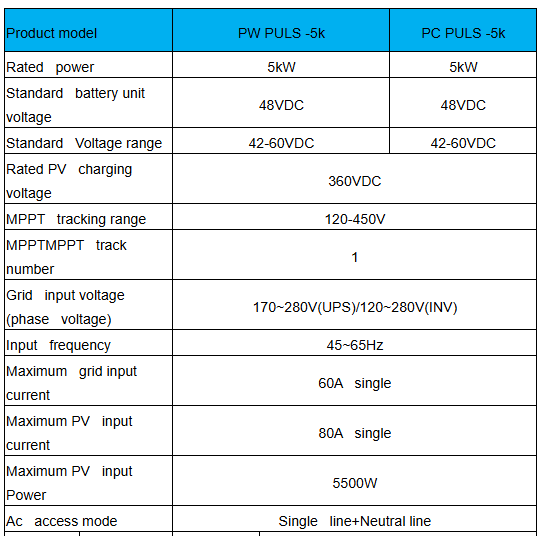
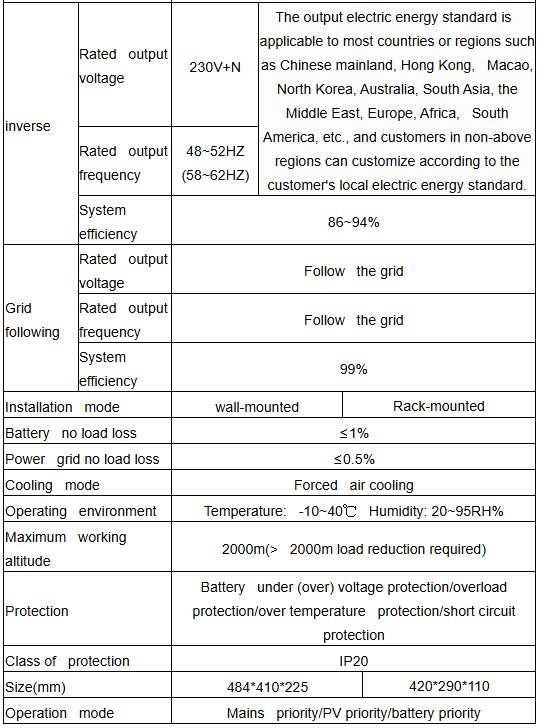
How does a PV inverter work?
A photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a high-performance device that primarily converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC).
DC Input: The DC power produced by solar panels is connected to the inverter's input via cables.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): The inverter incorporates Maximum Power Point Tracking technology, which dynamically adjusts the input voltage and current to ensure the maximum energy output under varying light conditions.
DC Boost: If the input DC voltage is too low, the inverter has a boosting circuit to raise the voltage to the required level.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): PWM technology is used to generate an AC waveform that approximates a sine wave. The power electronic devices inside the inverter, such as IGBTs or MOSFETs, switch on and off according to certain rules to produce AC.
AC Output: The generated AC power is filtered to remove high-frequency noise and is stabilized through voltage regulation circuits to ensure stable output voltage and frequency.
Grid-Tie Function: For grid-tied inverters, the output AC power can be fed directly into the electrical grid for residential or commercial use.









