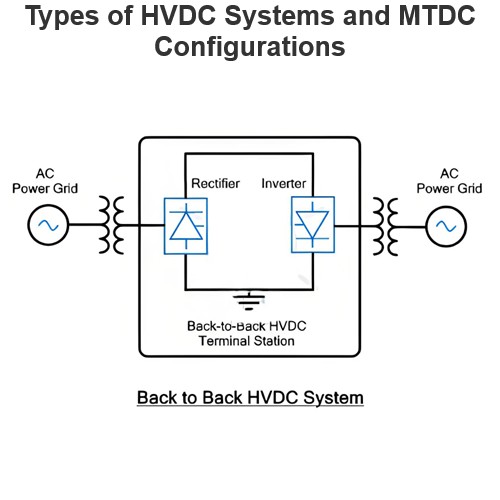
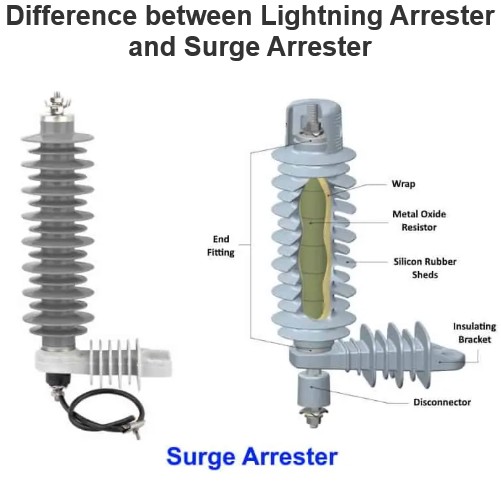
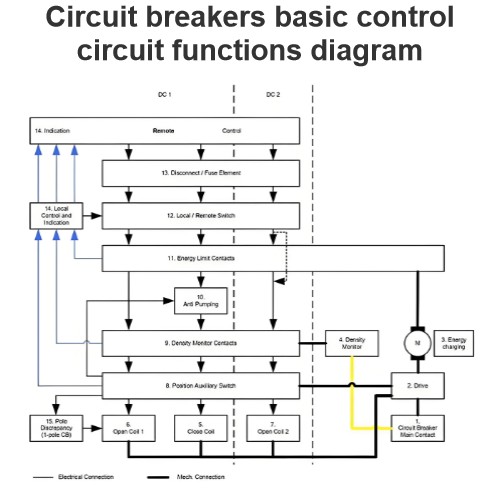
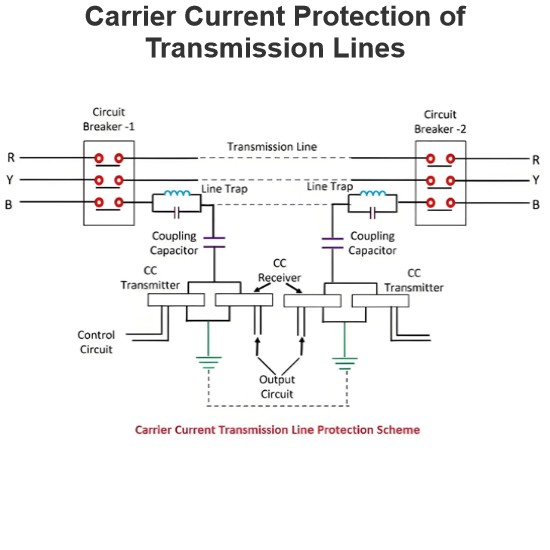
Medium Transmission Line
A transmission line is classified as a medium transmission line when its length exceeds 80 kilometers but remains below 250 kilometers. Along such lines, electrical parameters like resistance, inductance, and capacitance are uniformly distributed throughout their entire length. Given the significant length of medium transmission lines, the charging current becomes substantial, and the shunt admittance plays a crucial role in determining the line's effective electrical characteristics.
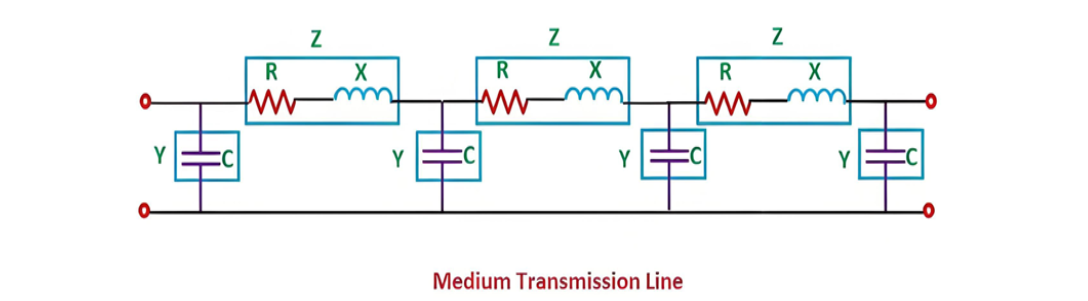
In the analysis and modeling of medium transmission lines, the shunt admittance and series impedance are often treated as lumped parameters. This simplification facilitates easier calculations and analysis while still capturing the essential electrical behavior of the line. The following diagram illustrates a typical configuration of a medium transmission line, highlighting how these lumped parameters are conceptually represented within the electrical model.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.