The utilization of Rogowski coils for current measurements, voltage dividers for voltage measurements, and a digital bus for sharing switchgear events and sampled measured values enables the separation of measuring hardware engineering from protection applications. This decoupling enhances flexibility and efficiency in electrical system design and operation.
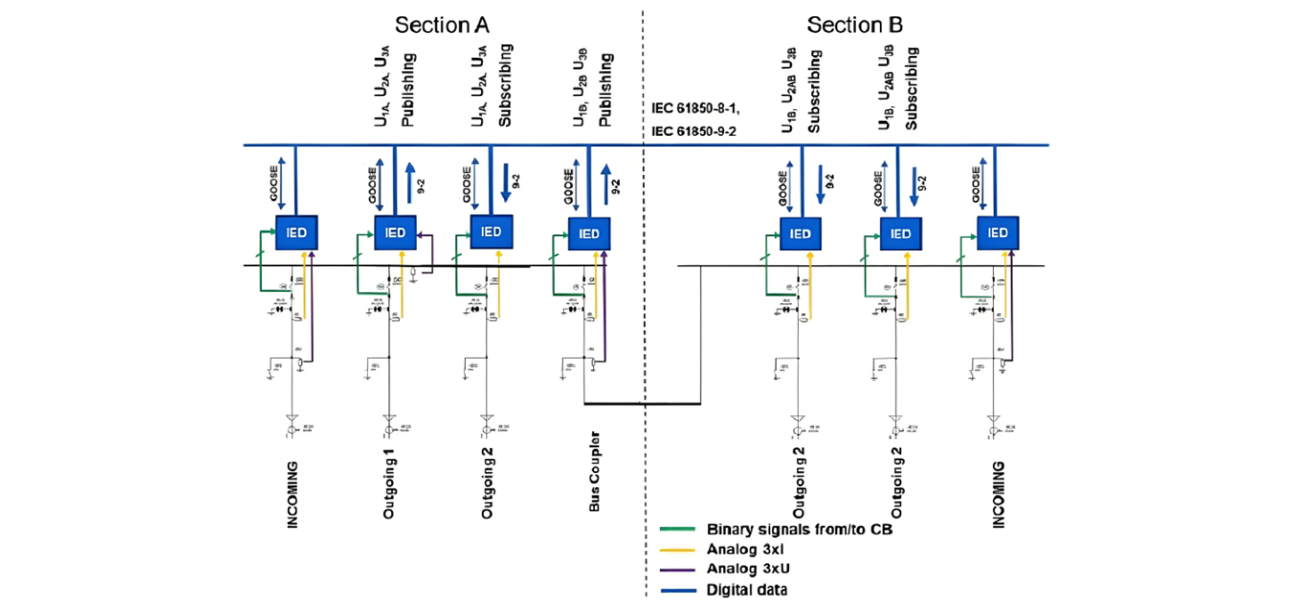
For the protection functions of each Intelligent Electronic Device (IED), line - to - ground currents are consistently measured separately in every feeder. In incoming feeders, resistive dividers are connected to the cables, supplying the necessary voltage measurements to the IEDs within these feeders.
Outgoing feeder protection schemes often require the use of busbar voltage measurements. For example, in section A, one outgoing feeder is equipped with resistive voltage dividers linked to the section A busbar system. Additionally, a bus coupler in this setup has resistive voltage dividers connected to the section B busbar system.
The IEDs in these feeders not only potentially utilize the measured voltage for their own protection schemes but also publish voltage - sampled measured data to the digital communication network. This allows all other IEDs, whether located in section A or B, to subscribe to this digital voltage measurement for their specific protection requirements.
Finally, switchgear events are shared across all feeders, which is crucial for implementing switchgear control, blocking, and interlocking logic. This sharing of information ensures coordinated and reliable operation of the switchgear, enhancing the overall safety and stability of the electrical system.

