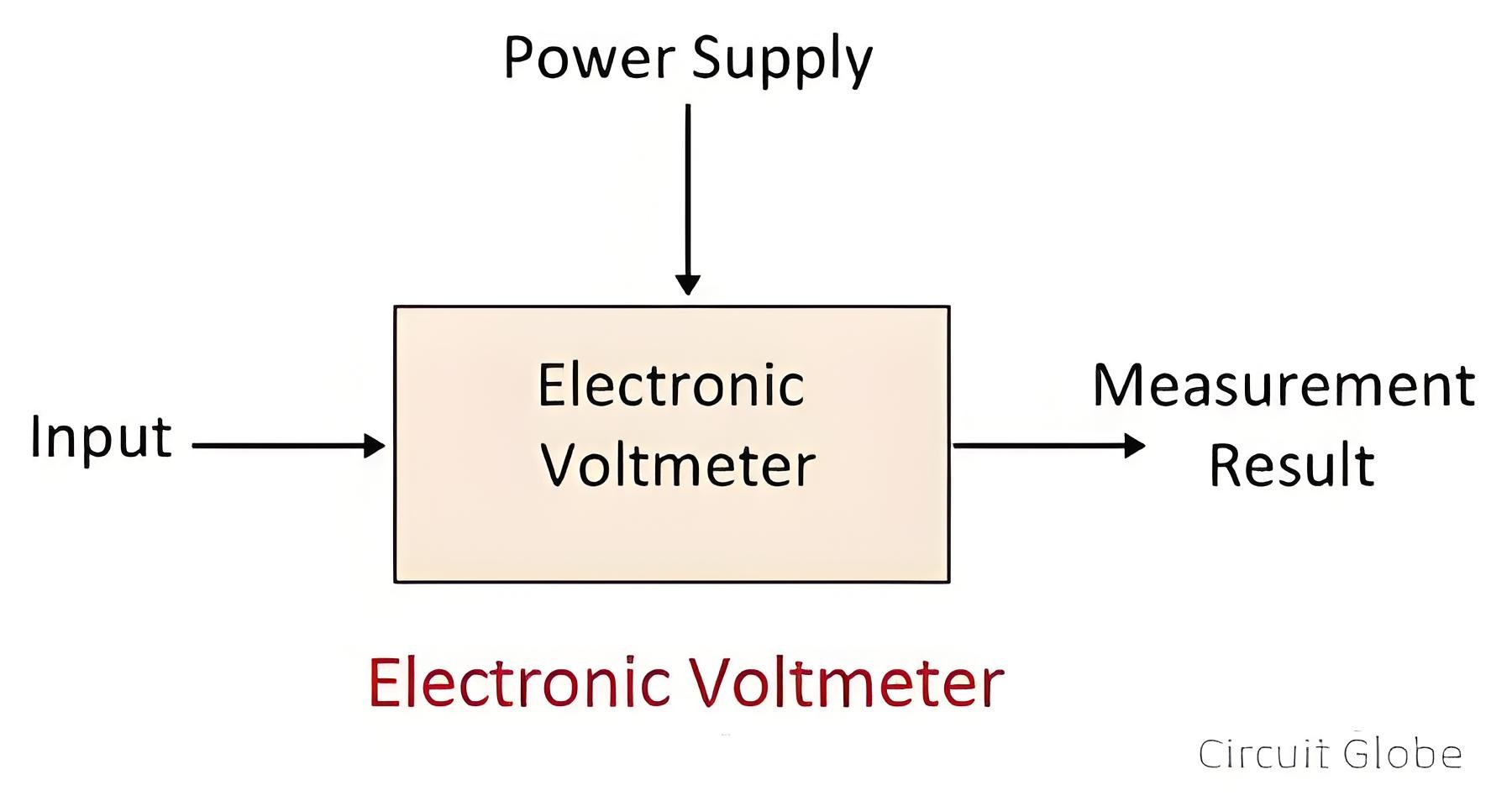
What is Electronic Voltmeter?
What is Electronic Voltmeter?
Definition
An electronic voltmeter is a voltmeter that utilizes an amplifier to enhance its sensitivity. It is capable of measuring the voltages of both AC and DC devices. Thanks to its high input resistance, the electronic voltmeter provides accurate readings.
A moving - coil voltmeter struggles to detect low voltages, but the electronic voltmeter overcomes this limitation. The electronic voltmeter has high input impedance, enabling it to detect signals of extremely weak strength and thus deliver accurate measurements. High impedance implies that the circuit resists the input supply.
Electronic voltmeters employ either transistors or vacuum tubes. A transistor - type voltmeter (TVM) has resistance, rendering it unsuitable for measuring current. In contrast, a vacuum voltmeter (VVM) has low resistance, making it suitable for current measurement.
Working of Electronic Voltmeter
The magnitude of the voltage being measured is directly proportional to the deflection of the pointer. The pointer is positioned on a calibrated scale, and the point to which the pointer deflects indicates the magnitude of the input voltage.
A moving - coil voltmeter draws a relatively large amount of power from the circuit under measurement, which can lead to errors in its readings. The electronic voltmeter addresses this issue.
In an electronic voltmeter, the pointer is deflected by drawing power from the auxiliary amplifier circuit. The output voltages of the amplifier circuit closely match the voltage of the test circuit. Since minimal additional power passes through the deflector, the meter provides accurate readings.
Types of Electronic Voltmeters
Electronic voltmeters are classified into two main types:
Analog Electronic Voltmeter
Digital Electronic Voltmeter
Analog Electronic Voltmeter
An analog electronic voltmeter is a voltage - measuring instrument that provides an output through the deflection of a pointer on a calibrated scale. It features high circuit impedance and employs an electronic amplifier to regulate the input signals. This type of voltmeter can be further divided into AC and DC analog electronic voltmeters.
Digital Electronic Voltmeter
A digital electronic voltmeter is a type of voltmeter that presents the measured voltage as a digital output reading, in the form of a numerical value. Digital electronic instruments minimize human and parallax errors since the reading is directly displayed in numeric form.
Advantages of Electronic Voltmeter
The electronic voltmeter offers several advantages, as follows:
Detection of Low - level Signals: The electronic voltmeter incorporates an amplifier, which helps avoid load errors. This amplifier can detect extremely small signals that generate a current of around 50μA. The ability to detect low - level signals is crucial for accurately determining the measured value.
Low Power Consumption: Electronic voltmeters utilize vacuum tubes and transistors with amplifying properties. They draw power from an auxiliary source for pointer deflection, while the voltage being measured controls the deflection of the sensing element. As a result, the circuit of the electronic voltmeter consumes very little power.
High - Frequency Range: Thanks to the use of transistors, the operation of the electronic voltmeter is not restricted by frequency range. In addition to voltage, it can measure signals with both very high and very low frequencies.
Power Measurement Requirement: The electronic voltmeter measures power only when the circuit is closed, meaning when current is flowing through the meter.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.