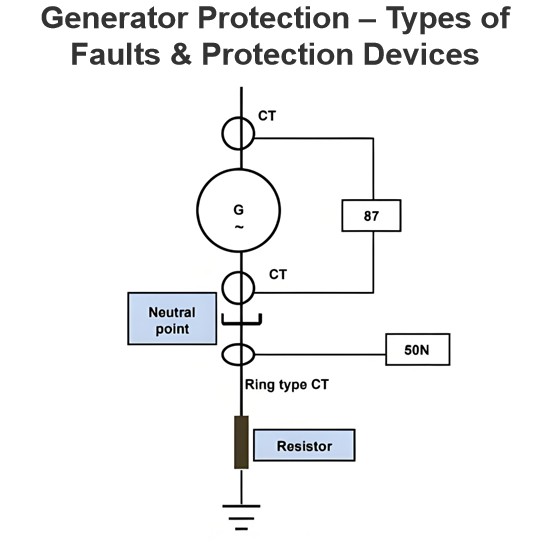
Slip Energy Recovery of an Induction Motor
Slip Energy Recovery, a sophisticated technique for regulating the speed of an induction motor, is alternatively referred to as the Static Scherbius Drive. In traditional rotor resistance control methods, during low-speed operation, the slip power within the rotor circuit is predominantly dissipated as I₂R losses, leading to significant energy waste and a notable reduction in system efficiency.By contrast, the slip energy recovery mechanism enables the capture of this otherwise wasted slip power from the rotor circuit and redirects it back to the AC source, allowing for its practical utilization outside the motor. This innovative approach not only mitigates energy loss but also substantially enhances the overall efficiency of the drive system.The diagram below illustrates the detailed connection configuration and operational methodology for slip energy recovery and power reclamation in an induction motor setup:
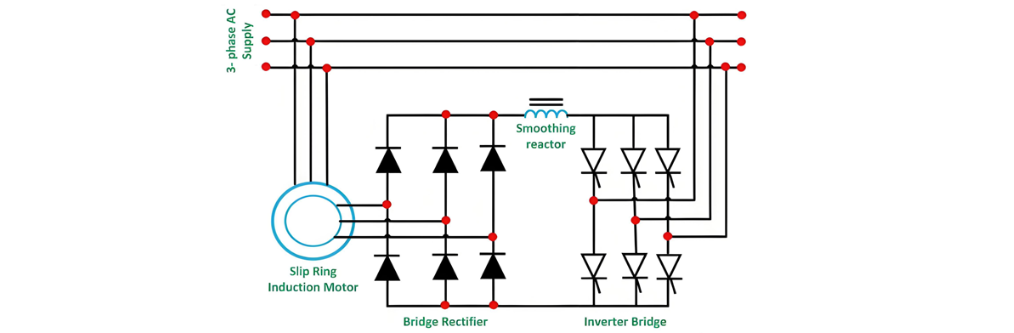
The fundamental principle of slip power recovery involves connecting an external electromotive force (EMF) source to the rotor circuit at the slip frequency. This technique enables speed control of a slip-ring induction motor below its synchronous speed. A portion of the rotor's alternating current (AC) power—known as slip power—is first converted to direct current (DC) via a diode bridge rectifier.A smoothing reactor is incorporated to stabilize the pulsating rectified current, ensuring a consistent DC output. This DC power is then fed into the inverter, which operates as a controlled rectifier in inversion mode. The inverter converts the DC power back to AC and redirects it to the main AC source, completing the energy recovery cycle.This speed control method is particularly suited for high-power applications where wide-range speed variations generate substantial slip power, making energy recovery both technically feasible and economically advantageous.