Speed Control of an Induction Motor
There are multiple methods for controlling the speed of an induction motor. The rotor speed of an induction motor is determined by the equation presented below. From equation (1), it becomes evident that the motor's speed can be modified by altering the frequency f, the number of poles P, or the slip s. To achieve the desired speed adjustment, one can employ any single method from the following list or combine multiple techniques. All of these induction - motor speed - control methods find practical applications in real - world scenarios.
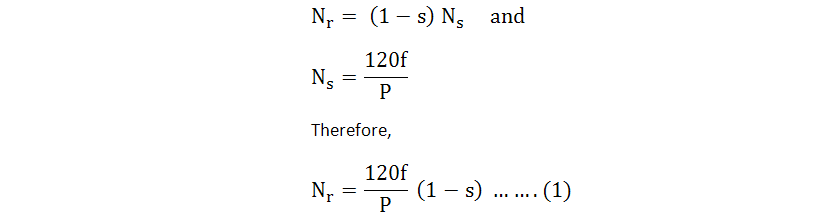
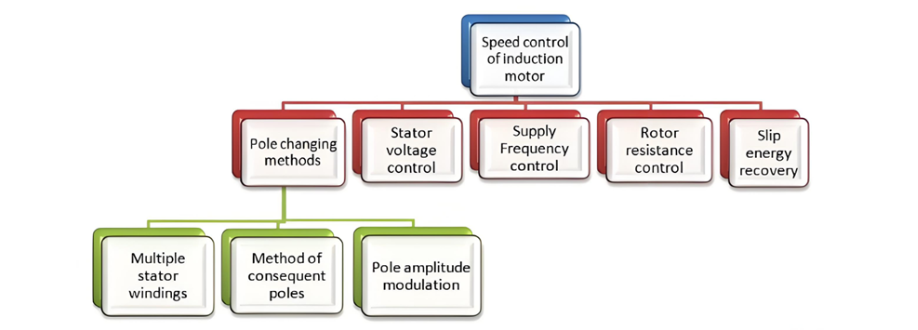
The speed - control methods for induction motors are as follows:
Pole Changing
The pole - changing method can be further categorized into three distinct types:
- Method of Consequent Poles: This approach leverages specific magnetic configurations to change the effective number of poles in the motor.
- Multiple Stator Windings: By utilizing different sets of windings on the stator, the number of poles can be adjusted, thereby influencing the motor's speed.
- Pole Amplitude Modulation: A more sophisticated technique that modulates the amplitude of the magnetic poles to achieve speed variation.
Other Methods
- Stator Voltage Control: Adjusting the voltage supplied to the stator can impact the motor's performance and speed.
- Supply Frequency Control: Altering the frequency of the electrical supply directly affects the rotational speed of the induction motor.
- Rotor Resistance Control: Modifying the resistance in the rotor circuit can change the motor's speed - torque characteristics and achieve speed control.
- Slip Energy Recovery: This method focuses on recovering and utilizing the energy associated with the slip to regulate the motor's speed more efficiently.
Each of these speed - control methods is described in detail in the relevant sections, providing an in - depth understanding of their operation, advantages, and applications.