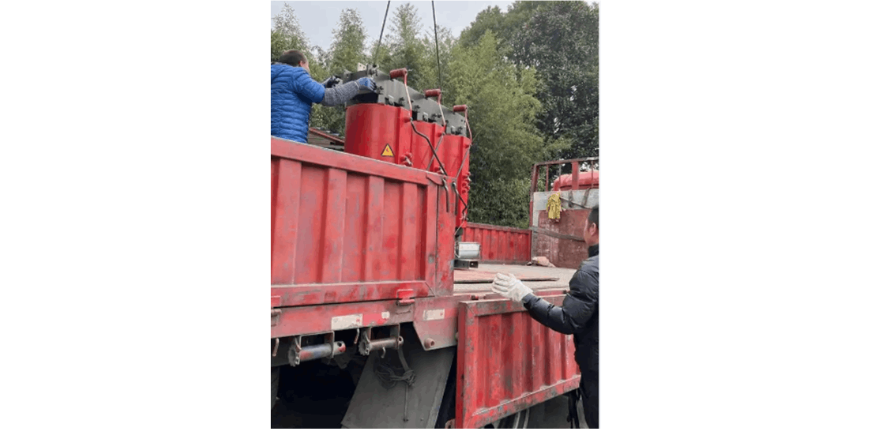
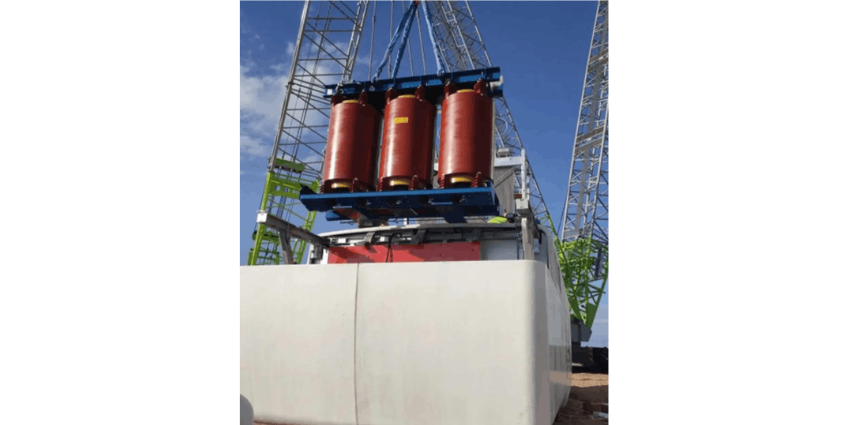
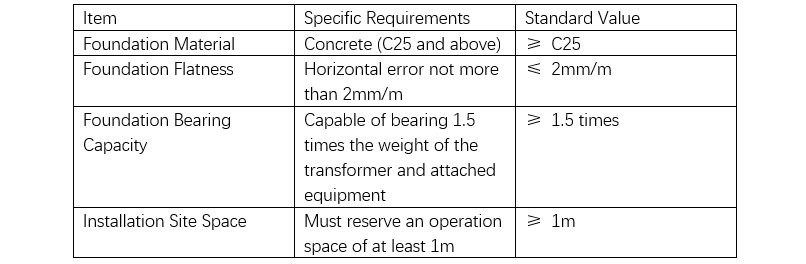
What aspects need attention during the installation of dry-type transformers?
James
07/01/2025
Professionalism builds strength. As an expert in the installation and operation of electrical equipment, I am proficient in the installation process and strictly adhere to standards. I skillfully master the operation essentials and can swiftly eliminate faults. With a heart that constantly explores new knowledge, I illuminate the path to the efficient operation of electrical equipment.

What tests are required for dry-type transformers?
1 Pre - commissioning InspectionAs a front - line tester, before formally commissioning a dry - type transformer, I need to carry out a comprehensive and systematic inspection. First, I conduct a visual inspection of the transformer body and its accessories, carefully checking for mechanical damage or deformation. Then, I check whether the leads of the high - and low - voltage windings are firmly connected and whether the bolt tightening torque meets the standard requirements (usually 40 - 60N&m
Oliver Watts
07/01/2025

What are the causes of dry-type transformers burning out during operation?
1 Fault PhenomenonI am engaged in front - line fault maintenance work, and recently encountered problems with dry - type transformers. Dry - type transformers have a simple structure, are convenient for transportation, and easy for maintenance. They are widely used in power distribution places with relatively high environmental protection requirements. Because of their good fire - resistance, they can be installed in load - center areas to reduce voltage loss and power loss.The property manageme
Felix Spark
07/01/2025

What is included in the operational procedures of a smart electricity meter load switch?
As a frontline operator who deals with smart electricity meters daily, I’m well - versed in the design and operational norms of load switches (both internal and external) in these meters. Below, I’ll break down the technical requirements and practical key points based on my on - site experience for easy reference.I. Basic Understanding of Internal and External Load SwitchesIn the type specifications for single - phase and three - phase smart electricity meters (such as environmental
James
06/28/2025

What are the key considerations for photovoltaic transformer selection?
Sizing Principles and Technical Parameters of Photovoltaic TransformersSizing photovoltaic transformers requires a comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, includingcapacity matching, voltage ratio selection, short - circuit impedance setting, insulation class determination, and thermal design optimization. The key sizing principles are as follows:(I) Capacity Matching: Fundamental for Load BearingCapacity matching is thecore prerequisitein sizing photovoltaic transformers. It requires a
Echo
06/27/2025