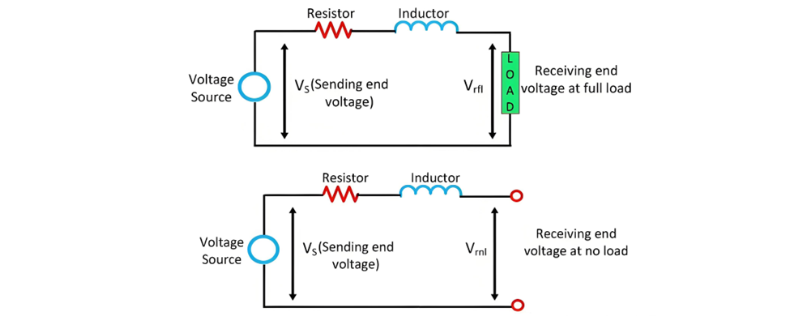
Definition: Voltage regulation (or line regulation) refers to the variation in voltage at the receiving end of a transmission line when the full load at a specified power factor is removed, with the sending-end voltage maintained constant. In simpler terms, it is the percentage change in the load-end voltage when transitioning from no-load to full-load conditions. This parameter is expressed as a fraction or percentage of the receiving-end voltage, serving as a critical metric for assessing the stability and performance of electrical power systems.
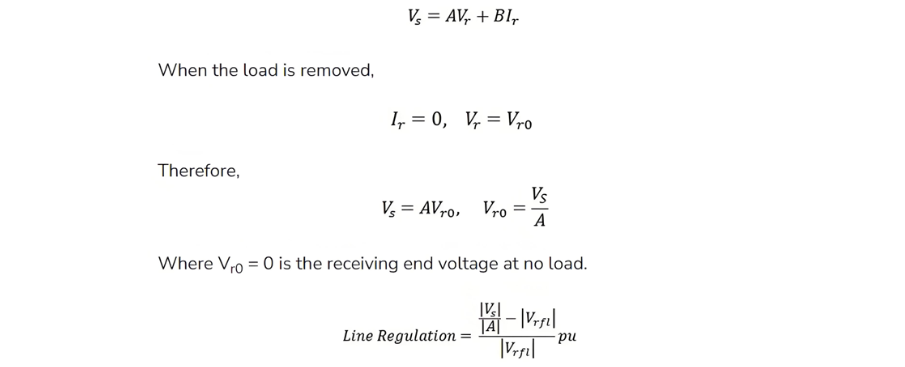
The line regulation is given by the equation shown below.
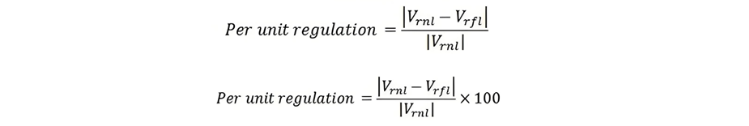
Here, ∣Vrnl∣ represents the magnitude of the receiving-end voltage at no load, and |Vrfl| represents the magnitude of the receiving-end voltage at full load.
Line voltage regulation is influenced by the load's power factor:
- Lagging Power Factor: The sending-end voltage exceeds the receiving-end voltage at full load, resulting in positive regulation.
- Leading Power Factor: The receiving-end voltage becomes higher than the sending-end voltage at full load, causing the line regulation to be negative (as the receiving-end voltage rises when the load is removed).
This phenomenon underscores how reactive power flow—dictated by power factor—alters voltage distribution along the transmission line.
Line Regulation for Short Lines:
For a short transmission line, the receiving-end voltage at no load ∣Vrnl∣ equals the sending-end voltage ∣VS∣ (assuming no significant reactive power effects). At full load,
The simplest method for measuring line regulation involves connecting three parallel resistors to the supply. Two resistors are linked to a switch, while the third is directly connected to the supply. The resistor values are selected such that the directly connected resistor has a high resistance, whereas the other two (connected in parallel via the switch) have nominal values. A voltmeter placed in parallel with each resistor measures the voltage across each line, providing data for calculating line voltage regulation.