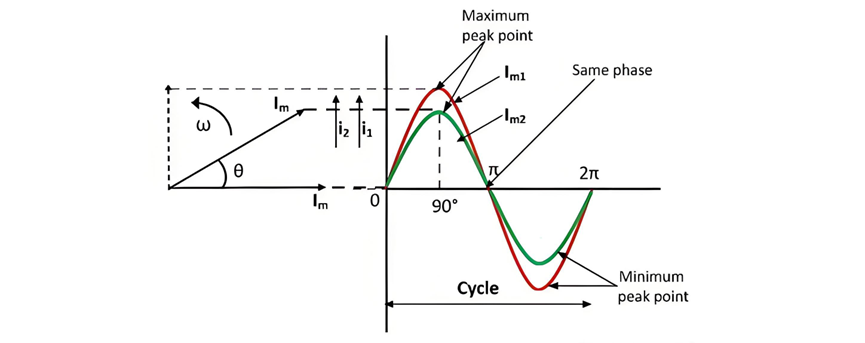
Definition: The phase of an alternating quantity represents the proportion of a complete cycle that the quantity has traversed relative to a designated reference origin. In the context of alternating electrical or physical phenomena, when two such quantities share identical frequencies, and their respective maxima (peaks) and minima (troughs) coincide precisely in time, these quantities are characterized as being in phase. This synchronization indicates a perfect temporal alignment, where the waveforms of the two quantities progress in unison without any relative displacement.
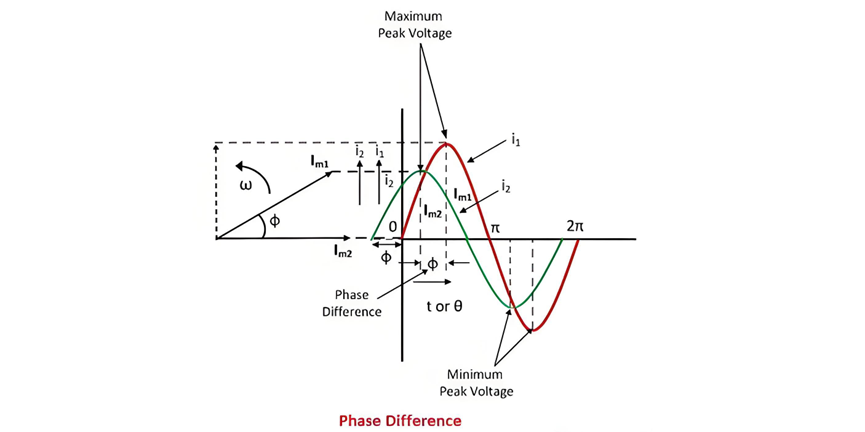
Examine the two alternating currents, Im1 and Im2, depicted in the figure below. These two electrical quantities not only reach their maximum and minimum amplitude peaks simultaneously but also cross the zero - value threshold precisely at the identical instant.
Phase Difference
Definition: The phase difference between two electrical quantities is defined as the angular disparity between the maximum values of two alternating quantities that share the same frequency.
Put differently, two alternating quantities exhibit a phase difference when, despite having identical frequencies, they reach their zero - crossing points at distinct moments. The angular separation between the zero - value instants of these two alternating quantities is referred to as the angle of phase difference.
Take, for instance, the two alternating currents with magnitudes Im1 and Im2, represented in vector form. Both vectors rotate at a consistent angular velocity of ω radians per second. Since these two currents cross the zero - value mark at different times, they are said to possess a phase difference denoted by the angle φ.
The quantity that reaches its positive maximum value ahead of another is termed the leading quantity. Conversely, the quantity that attains its positive maximum value after the other is referred to as the lagging quantity. In this context, current Im1 leads current Im2; equivalently, current Im2 lags behind current Im1.
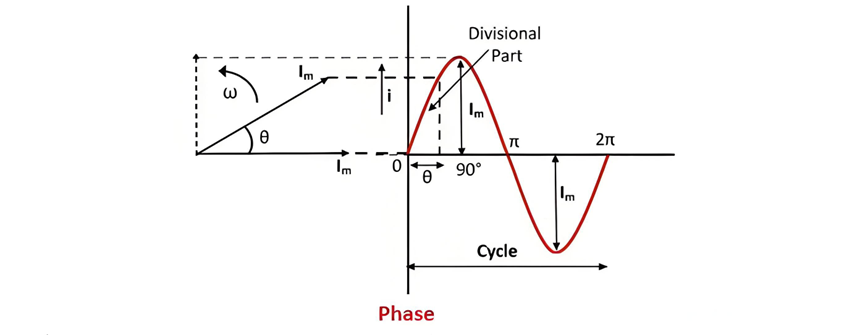
Cycle: An alternating quantity is considered to have completed a full cycle when it traverses through an entire sequence of positive and negative values or spans 360 electrical degrees.