Critical Clearing Angle
The critical clearing angle is defined as the maximum allowable variation in the load angle curve during a fault, beyond which system synchronism is lost if the fault is not cleared. In essence, when a fault occurs in an electrical system, the load angle begins to increase, putting the system at risk of instability. The specific angle at which clearing the fault restores system stability is referred to as the critical clearing angle.
For a given initial load condition, there exists a specific critical clearing angle. If the actual angle at which the fault is cleared exceeds this critical value, the system will become unstable; conversely, if it remains within the critical threshold, the system will maintain its stability. As illustrated in the diagram below, curve A represents the power - angle relationship under normal, healthy operating conditions. Curve B depicts the power - angle curve during a fault, while curve C shows the power - angle behavior after the fault has been isolated.
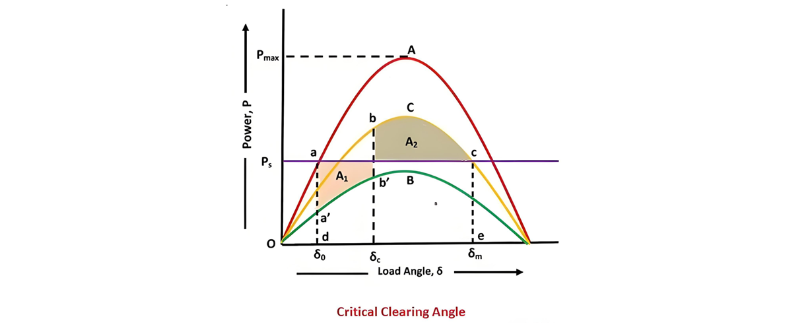
Here, γ1represents the ratio of the system reactance during normal (healthy) operation to the reactance when a fault occurs. Meanwhile, γ2 denotes the ratio of the steady - state power limit of the system after the fault has been isolated to that of the system under its initial operating condition.Regarding the transient stability limit, a key criterion is that two specific areas are equal, i.e., A1 = A2. To elaborate, the area under the curve adec (shaped like a rectangle) must match the area under the curve da'b'bce. This equality of areas serves as a fundamental condition for assessing whether the power system can maintain stability during and after a transient fault event, ensuring that the energy imbalances introduced by the fault can be properly managed to prevent system collapse.

Thus if γ1, γ2, and δ0 are known, the critical clearing angle δc can be determined.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.