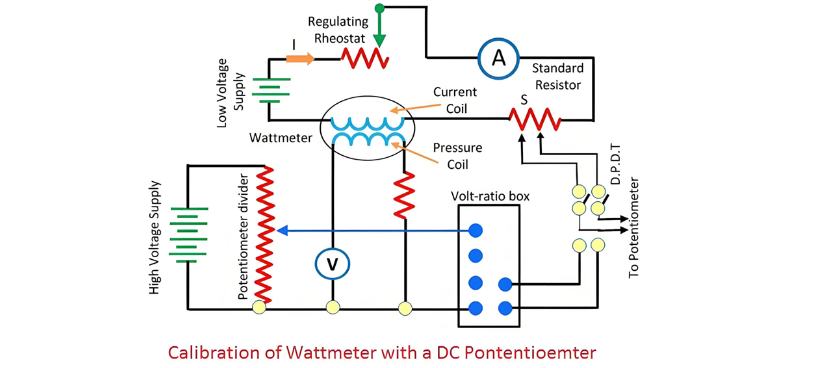
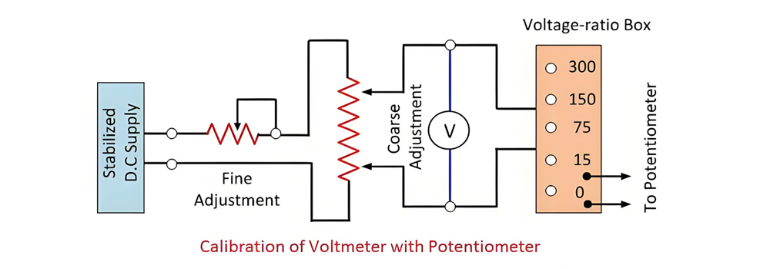
Calibration of Voltmeter, Ammeter & Wattmeter using Potentiometer
Calibration is the process of verifying the accuracy of a result by comparing it with a standard value. In essence, it assesses the correctness of an instrument by contrasting it against a reference standard. This process enables us to identify errors in readings and make adjustments to voltages to achieve an ideal reading.
Calibration of Voltmeter
The circuit for the calibration of the voltmeter is shown in the figure below.
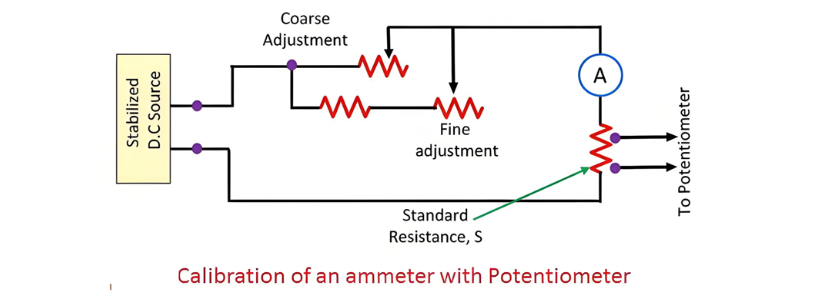
A standard resistance is connected in series with the ammeter that is to be calibrated. A potentiometer is utilized to measure the voltage across the standard resistor. The current flowing through the standard resistance is determined by the formula described below.
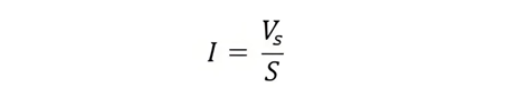
where:Vs is the voltage across the standard resistor, as measured by the potentiometer.S is the resistance value of the standard resistor.This approach to ammeter calibration is highly accurate. The reason lies in the fact that both the value of the standard resistance and the voltage measured by the potentiometer can be precisely determined by the measuring instruments.Calibration of WattmeterThe circuit employed for calibrating the wattmeter is depicted in the figure below.