| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | High Voltage Current-Limiting Fuse(For full range&transformer protection) |
| Rated voltage | 36kV |
| Rated normal current | 50A |
| Breaking capacity | 40kA |
| Series | Current-Limiting Fuse |
Characteristic brief :
Rated voltage from 7.2KV to 40.5KV.
Wide range of rated current from 6.3A to 200A.
Full range performance options available at 12KV and 24KV.
Powerful pyrotechnic or spring striker.
H.R.C.
Gurrent-limiting.
Low power dissipation,low temperature rise.
Operation extremely quickly,high reliability.
With primary coil of transformer in series.
Isolating & protecting transformer.
Conforming to standards: GB15166.2 DIN43625 BS2692-1 IEC60282-1.
Model illustration:
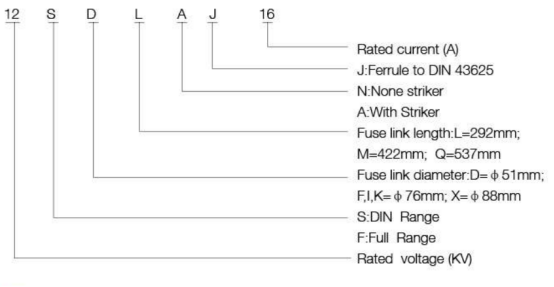
Technical Parameters:
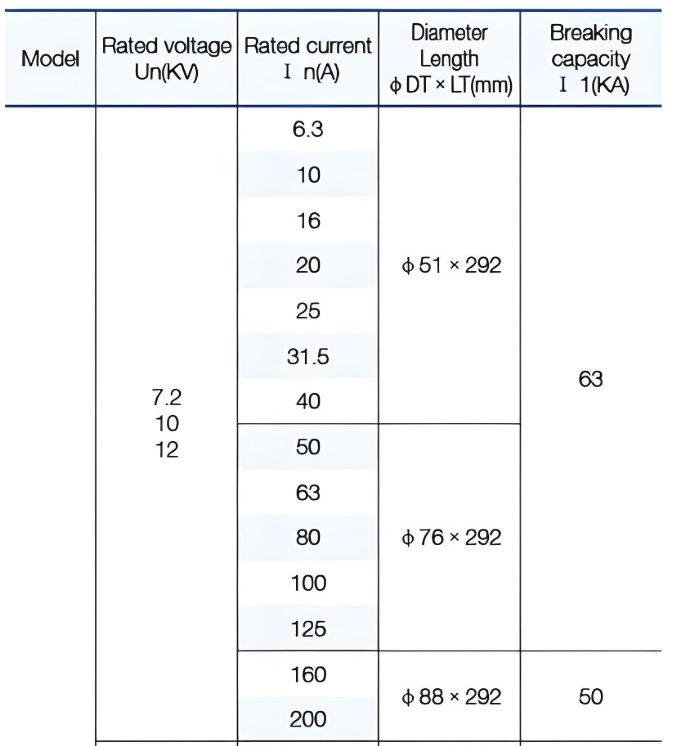
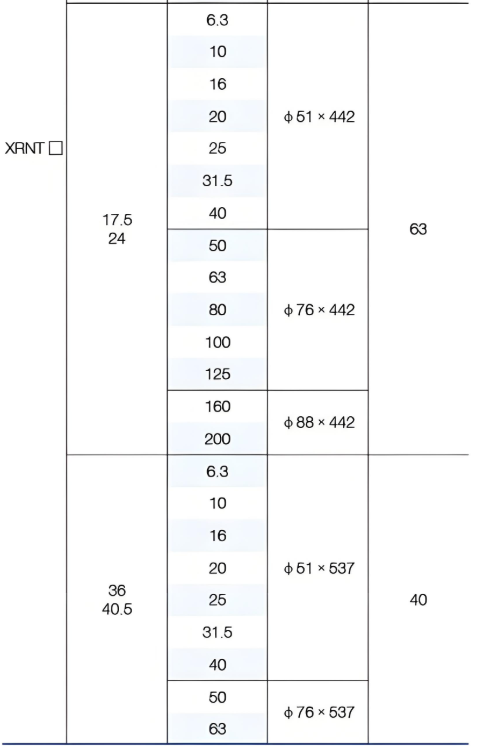
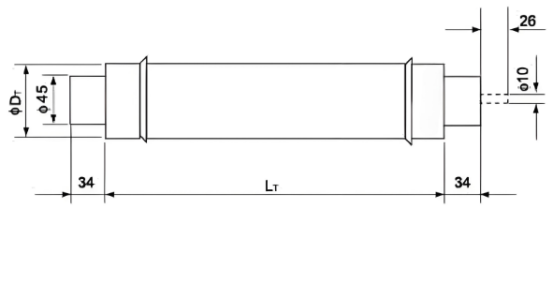
External&installation dimensions(Unit:tmm)
XRNT Fuse link
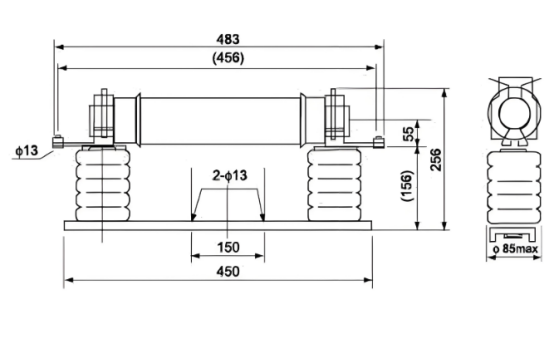
XRNT -12KV/ Fuse base
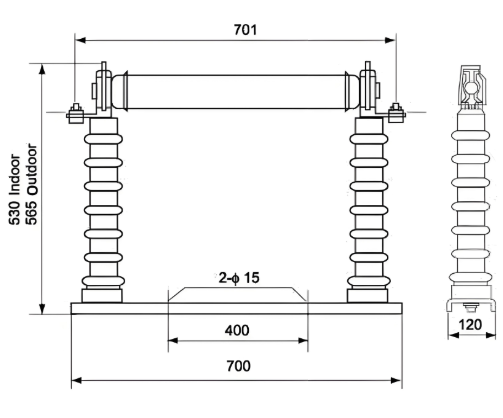
XRNT -40.5KV/ Fuse base
What are the structural features of the high-voltage current-limiting fuses (for the full range and transformer protection)?
The fusible element is a critical component, typically made from materials with high conductivity and a low melting point, such as silver or copper alloys. Its design is intricate, often featuring multiple narrowed sections that will melt first when subjected to overload or short-circuit currents. This design enables the fuse to respond rapidly to fault currents, effectively limiting the rise in current.
The interior is filled with arc-quenching media such as quartz sand. Quartz sand possesses excellent insulation and thermal conductivity properties. When the fusible element melts and an arc is generated, the quartz sand absorbs the heat from the arc, rapidly cooling and extinguishing it, thereby interrupting the current flow and preventing damage from sustained arcing.
The enclosure is generally made from high-strength ceramics or composite insulating materials. Ceramic enclosures offer superior insulation performance and mechanical strength, capable of withstanding the pressure generated during internal arc quenching. Additionally, the excellent sealing performance prevents external environmental factors (such as moisture and dust) from affecting the internal arc-quenching medium and the fusible element.






