| Brand | ROCKWILL |
| Model NO. | 550KV GIS Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) |
| Rated voltage | 550kV |
| Rated normal current | 6300A |
| Series | ZF27 |
Description:
The ZF27 - 550, an independently developed 550KV - level Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS), boasts technical parameters at the international leading edge. Tailored for 550KV power systems, it enables seamless control, measurement, and protection. Comprising key components like circuit breakers, disconnectors, earthing switches, quick earthing switches, current transformers, busbars, and air - insulated bushings for power inlets and outlets, other components are enclosed in an earthed shell with SF6 gas serving as both arc - extinguishing and insulating medium. It can be flexibly configured into various connection modes per user needs.
Main Features:
The circuit breaker features a single - fracture arcing chamber with a simple, rational structure and advanced technology.
It offers robust breaking capabilities, an extended electrical contact lifespan, and a long service life.
The circuit breaker unit can be installed on - site without opening the chamber and filled with SF6 gas directly, preventing dust and foreign matter ingress.
The innovative hydraulic operating mechanism has minimal external piping, reducing the likelihood of oil leakage.
During operation, the hydraulic operating mechanism is automatically regulated by the pressure switch, maintaining a constant rated oil pressure regardless of ambient temperature. Its relief valve safeguards against overpressure risks.
In case of pressure loss, the hydraulic operating mechanism prevents slow tripping during pressure restoration.
The closing resistance of the product can be optionally installed or removed based on user requirements.
Technical Parameters:
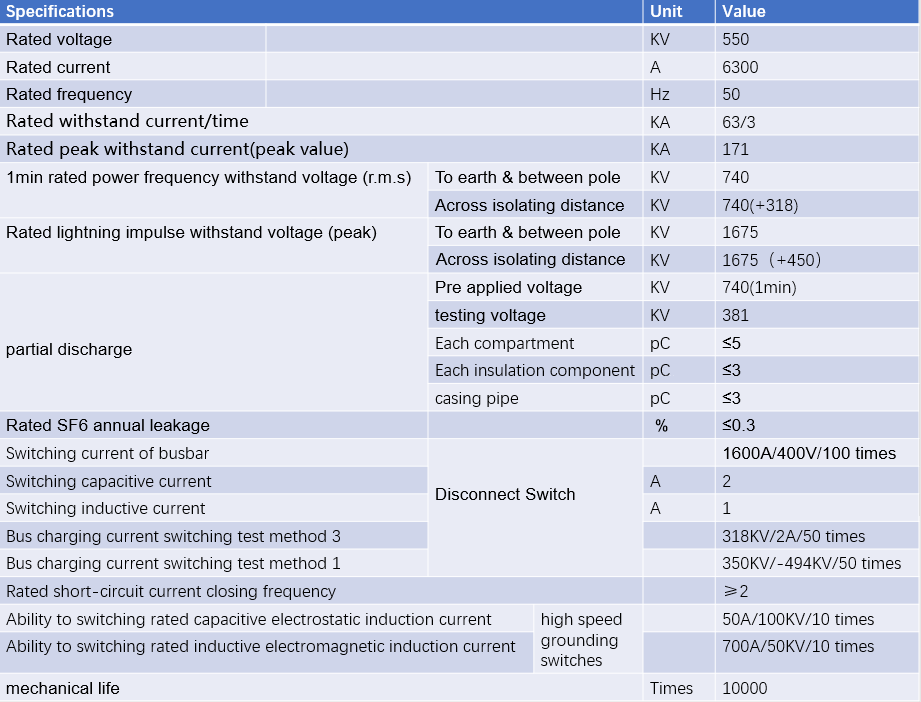
What are the technical parameters of gas-insulated Switchgear?
Rated Voltage:
Common rated voltage levels include 72.5kV, 126kV, 252kV, 363kV, and 550kV. The rated voltage determines the maximum operating voltage that the equipment can withstand and is a crucial factor in the design and selection of GIS (Gas-Insulated Switchgear) equipment. It must match the voltage level of the power system to ensure that the equipment operates safely and reliably under both normal and fault conditions.
The rated current ranges from a few hundred amperes to several thousand amperes, such as 1250A, 2000A, 3150A, 4000A, etc. The rated current indicates the maximum current that the equipment can carry continuously without damage. When selecting the equipment, it is necessary to consider a certain margin based on the actual load conditions to ensure that the equipment does not fail due to overload during normal operation and can also meet future load growth requirements.
Typically, the rated short-circuit breaking capacity ranges from 31.5kA to 63kA or even higher. This parameter measures the equipment's ability to interrupt short-circuit currents. When a short-circuit fault occurs in the power system, the short-circuit current increases dramatically. The GIS equipment must be able to quickly and reliably interrupt the short-circuit current to prevent the fault from escalating. The rated short-circuit breaking capacity must be greater than the maximum possible short-circuit current in the system to ensure the safety performance of the equipment during a short-circuit condition.
The rated pressure of SF₆ gas in the equipment is generally between 0.3MPa and 0.7MPa. The actual operating pressure may be adjusted according to the specific requirements of the equipment and environmental factors such as temperature. During operation, it is necessary to monitor and control parameters such as the pressure, humidity, and purity of the SF₆ gas to ensure they remain within specified limits. This ensures the insulation and arc-quenching performance of the equipment.






