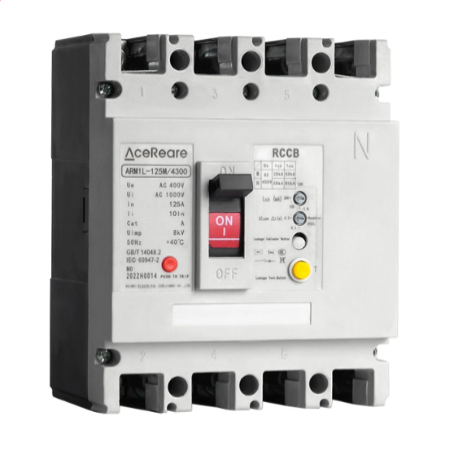
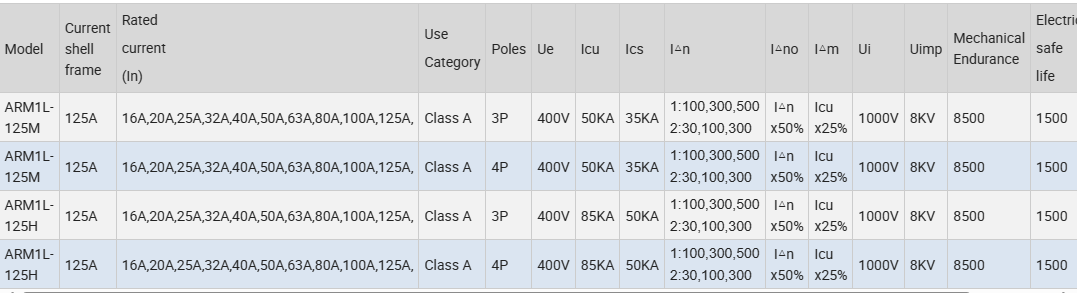
| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | Residual Current ProtectedMolded Case Circuit Breaker |
| Rated voltage | 400V |
| Rated normal current | 125A |
| Series | Arm1L |
Description
Residual current circuit breaker, mainly applicable to AC 50Hz, rated voltage 400V, rated current up to 800A in the distribution network, used to provide indirect contact protection to people, can also be used to prevent fire hazards caused by equipment insulation damage, resulting in ground fault current, and can be used to distribute electrical energy and protect the line and power supply equipment overload and short circuit, but also as the line of infrequent conversion and motor Infrequent switching and motor starting. Conventional leakage protection module with residual current protection circuit breaker work power sampling for two-phase, this series of circuit breakers for three-phase, if the lack of a phase, circuit breaker leakage protection module can still work normally; rated residual action current and maximum disconnection time according to the actual situation on site adjustable; when the phase voltage is reduced to 50V, leakage protection module can still work normally
Basic Info.
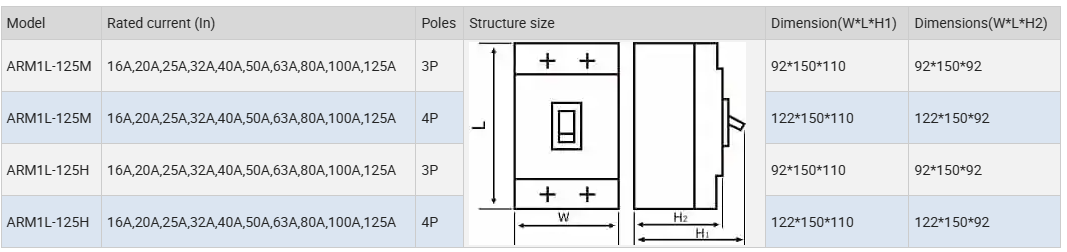
External dimensions
Environmental requirement
1,The surrounding air temperature state is: -5ºC~+40ºC
2,The altitude of the installation site does not exceed 2000m
3,The relative humidity of the air at the installation site does not exceed 50% at the highest temperature of +40ºC, and can have a higher relative humidity at lower temperatures, such as up to 90% at 20ºC. Special measures should be taken for the occasional condensation due to temperature changes.
4,The pollution level is 3
5, wet and hot band type (TH type) circuit breakers through GB/T2423.4, GB/T2423.18 test requirements, can withstand the effects of humid air, salt spray, oil mist, mold.
6,The circuit breaker should be installed in a place where there is no danger of explosion and no conductive dust, not enough to corrode the metal and destroy the insulation
7, the circuit breaker should be installed in a place where there is no rain or snow intrusion
8,Operating conditions: the circuit breaker passes the test requirements of GB/T 2423.1 and GB/T2423.2, the surrounding air temperature can be as low as -25ºC (ARM1DC/ARM3DC/ARM6DC can provide temperature as low as -40ºC, consult our company), as high as +70ºC (more than 40ºC reduced capacity use, see the technical information in the attached sample)
Product show







