Coordination of Reclosers and Sectionalizers in Distribution Networks
Automatic reclosers and automatic sectionalizers (reclosers and sectionalizers for short) are relatively complete and highly reliable automated devices. They can not only reliably and promptly eliminate transient faults but also minimize the power outage range caused by permanent faults. Since reclosers and sectionalizers are used in distribution networks, they can selectively and effectively eliminate transient faults to prevent them from developing into permanent faults and can also isolate permanent faults, thus greatly improving power supply reliability.
1. Functions and Features of Automatic Reclosers
An automatic recloser is an automated device with protection, detection, and control functions. It has inverse time - current characteristic curves with different time limits and a multiple - reclosing function. It is a new type of electromechanical integration electrical appliance that integrates a circuit breaker, relay protection, and an operating mechanism. It can automatically detect the current through the main circuit of the recloser. When a fault current is confirmed, it will automatically interrupt the fault current according to the inverse time protection after a certain period and automatically reclose multiple times as required to restore power supply to the line. If the fault is transient, the line will return to normal power supply after the recloser recloses; if the fault is a permanent fault, after the recloser completes the preset number of reclosing operations (usually 3 times) and confirms that the line fault is a permanent fault, it will automatically lock out and no longer supply power to the faulty line until the fault is eliminated and the reclosing lockout is manually released to restore the normal state.
The specific functions and features of reclosers are as follows:
- In terms of breaking performance, reclosers have functions such as breaking short - circuit currents, performing multiple reclosing operations, selecting the sequential coordination of protection characteristics, and resetting the protection system.
- A recloser is mainly composed of an arc - extinguishing chamber, an operating mechanism, a control system, a closing coil, and other parts.
- A recloser is a local control device. In terms of protection and control characteristics, it has functions such as self - fault detection, judging the nature of the current, executing switching operations, and can return to the initial state, memorize the number of operations, and complete the selection of operation sequences such as closing lockout. For reclosers used on lines, there is no additional operating device, and their operating power is directly taken from the high - voltage line. For those used in substations, there is a low - voltage power supply for the opening and closing of the operating mechanism.
- Reclosers are suitable for outdoor distribution line installation methods and can be installed either in substations or on various poles.
- The number of locking operations, the opening speed characteristics, and the reclosing operation sequence of different types of reclosers are generally different. Their typical characteristic of 4 break operations and 3 reclosing operations is: break → (T₁) close - break → (T₂) close - break → (T₃) close - break, where T₁ and T₂ are adjustable and vary with different products. It can adjust the number of reclosing operations and the reclosing interval time according to the needs during operation.
- The phase - to - phase fault breaking of reclosers adopts the inverse time characteristic to cooperate with the ampere - time characteristic of fuses (but the ground fault breaking of electronically controlled reclosers generally adopts the definite time limit). Reclosers have two types of ampere - time characteristic curves: fast and slow. Usually, its first breaking operation acts according to the fast curve, so that it can cut off the fault current within 0.03 - 0.04s. For subsequent breaking operations, different ampere - time characteristic curves can be selected according to the needs of protection coordination.
2. Functions and Features of Automatic Sectionalizers
A sectionalizer is an automatic protection device used in a distribution system to isolate the faulty line section. It is usually used in cooperation with an automatic recloser or a circuit breaker. A sectionalizer cannot break fault currents. When a fault occurs in a sectioned line, the backup protection recloser or circuit breaker of the sectionalizer operates, and the counting function of the sectionalizer starts to accumulate the number of tripping operations of the recloser. When the sectionalizer reaches the preset number of recorded operations, it will automatically trip at the moment the backup device trips to disconnect the faulty line section. The recloser recloses again to restore power supply to other lines. If the number of tripping operations of the recloser does not reach the preset number of recorded operations of the sectionalizer and the fault has been eliminated, the accumulated count of the sectionalizer will automatically disappear after a period of time, returning to the initial state.
Sectionalizers are divided into two types according to the number of phases: single - phase and three - phase. According to the control method, they are divided into hydraulic control and electronic control. Hydraulically controlled sectionalizers use hydraulic control for counting, while electronically controlled sectionalizers use electronic counting. The main functions and features of automatic sectionalizers are as follows:
- Sectionalizers have the function of automatically counting the number of tripping operations of the upper - level protection device.
- A sectionalizer cannot isolate fault currents, but it can disconnect permanent line faults in cooperation with a recloser. Since it can isolate full - load currents, it can be used as a manually operated load switch.
- A sectionalizer can perform automatic and manual tripping. After tripping, it is in a locked state and can only restore power supply through manual closing.
- A sectionalizer has a tripping coil connected in series in the main circuit, and the minimum operating current can be changed by replacing the coil.
- There is no mechanical or electrical connection between a sectionalizer and a recloser, and there is no restriction on its installation location.
- A sectionalizer does not have an ampere - time characteristic, so it has special advantages in use. For example, it can be used in occasions where the protection characteristic curves of two protection devices are very close, thus making up for the defect that coordination cannot be achieved sometimes even by adding steps in a multi - level protection system.
3. Cooperation Between Reclosers and Sectionalizers
The cooperative operation of reclosers and sectionalizers can realize the elimination of transient faults, the isolation of permanent fault areas, and ensure the normal power supply of non - faulty line segments. Due to the different functions of reclosers and sectionalizers, first, the section layout of the line should be reasonably determined according to the system operation conditions to improve the degree of distribution line automation and power supply reliability. Its typical structure is shown in Figure 1.
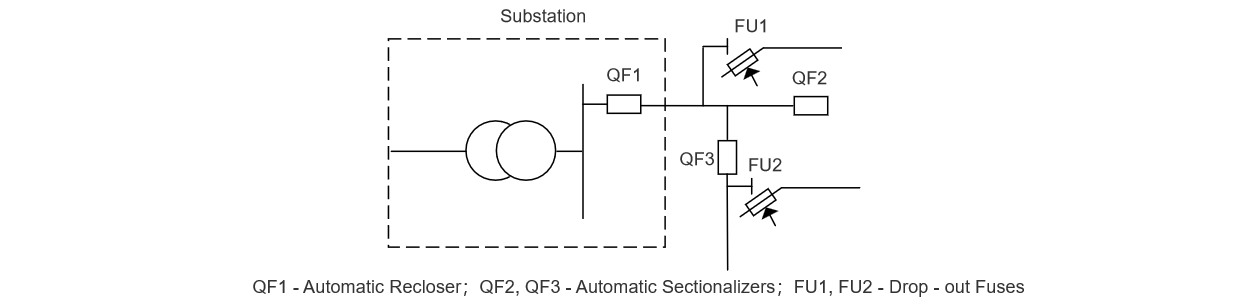
Theoretically speaking, each branch point on the line should be considered as a sectioning point. In this way, even if a permanent fault occurs on a relatively short branch line, it can be selectively sectioned, and the normal power supply of other sections can be maintained. However, due to economic and operating condition constraints, it is often impossible to achieve this. Therefore, it is necessary to proceed from reality and adapt to local conditions. Both reclosers and sectionalizers are intelligent devices with many advantages such as a high degree of automation. However, they can only play their roles when used in correct coordination. Therefore, the following coordination principles should be followed:
- The sectionalizer must be connected in series with the recloser and installed on the load side of the recloser.
- The backup recloser must be able to detect and act on the minimum fault current within the protection range of the sectionalizer.
- The starting current of the sectionalizer must be less than the minimum fault current within its protection range.
- The thermal stability rating and dynamic stability rating of the sectionalizer must meet the requirements.
- The starting current of the sectionalizer must be less than 80% of the minimum tripping current of the backup protection and greater than the peak value of the expected maximum load current.
- The number of recording times of the sectionalizer must be at least 1 time less than the number of tripping times of the backup protection before locking.
The memory time of the sectionalizer must be greater than the total accumulated fault breaking time (TAT) of the backup protection. The total accumulated time (TAT) of the backup protection action is the sum of the fault current - carrying time of each fault in the backup protection sequence and the reclosing interval. Since the sectionalizer does not have an ampere - time characteristic, the coordination between the recloser and the sectionalizer does not require the study of protection curves.
The backup protection recloser is set to lock after 4 tripping operations. These operations can be a combination of any fast and slow (or delayed) operation modes, and the setting number of times for the sectionalizer is selected as 3 counts. If a permanent fault occurs on the line on the load side of the sectionalizer, the sectionalizer will open to isolate the fault before the 3rd reclosing of the recloser, and then the recloser will supply power to the non - faulty line. If there are other serially configured sectionalizers, the number of locking times they are set with should be smaller level by level.
When a fault occurs on the line on the load side of the last - stage sectionalizer, the recloser acts. The serially connected sectionalizers all record the number of times the recloser breaks the current. After the last - stage sectionalizer reaches the number of action times, it trips to isolate the fault, and then the recloser recloses to connect the non - faulty line and restore normal power supply. The sectionalizers that do not reach the number of counting times will reset to the initial state after the specified reset time.