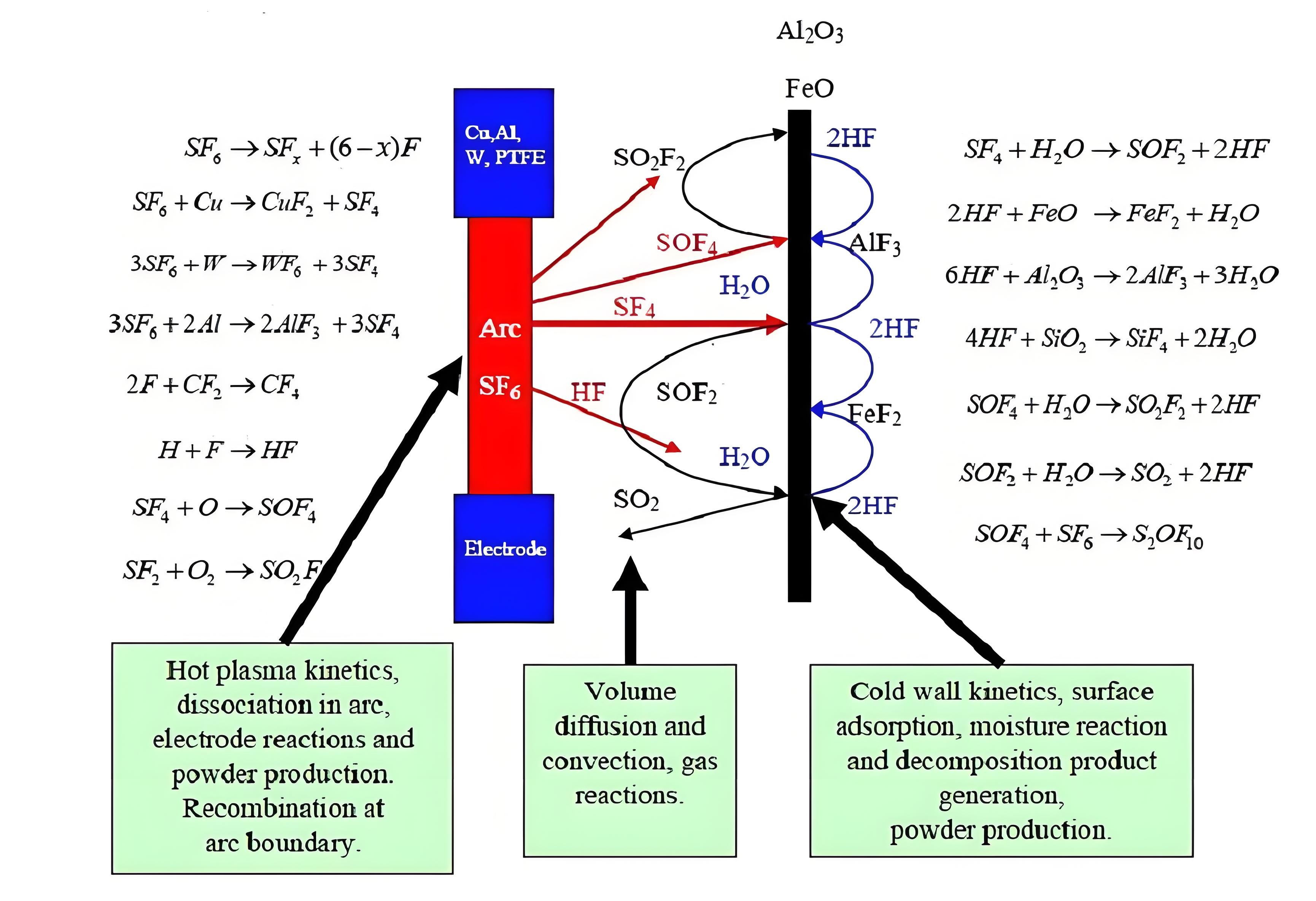
SF6 decomposition products from electrical arc in gas switchgear
Edwiin
03/19/2025

Analysis of the Technical Characteristics of Online Monitoring for Medium-Voltage Switchgear Status
With the increasing complexity of power system operation environment and the deepening of power system reform, traditional power grids are accelerating the transformation to smart grids. The goal of equipment condition-based maintenance is achieved through real-time perception of equipment status by new sensors, reliable communication via modern network technology, and effective monitoring by background expert systems.I. Analysis of Condition-based Maintenance StrategyCondition-based Maintenance
Oliver Watts
06/11/2025

What is the current application status and development trend of medium-voltage switchgear?
With the accelerated automation of power equipment, various medium-voltage switchgear have emerged in the market. Classified by insulation media, they are mainly divided into air-insulated, SF₆ gas-insulated and solid-insulated types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages: solid insulation offers good performance but poor environmental friendliness, SF₆ features excellent arc extinguishing capability but is a greenhouse gas, and air insulation has high cost-performance but larger volume
Echo
06/11/2025

What components make up the design of medium-voltage ring network distribution switchgear?
As an expert who has been deeply engaged in the field of power system design for many years, I have always paid attention to the technological evolution and application practice of medium-voltage ring main distribution equipment. As a core electrical device in the secondary distribution link of the power system, the design and performance of such equipment are directly related to the safe and stable operation of the power supply network. The following is a professional analysis of the key design
Dyson
06/11/2025

What aspects should be paid attention to when installing medium-voltage switch cabinets during the initial stage of subway operation?
1. Statistics on Common Faults of Medium-Voltage Switchgear in the Early Operation StageAs project participants, we found during the early operation of a new metro line: 21 sets of power supply equipment were put into use, with a total of 266 accident phenomena in the first year. Among them, 77 faults occurred in medium-voltage switchgear, accounting for 28.9%—significantly higher than faults in other equipment. Statistical analysis shows that major fault types include: protection device s
Felix Spark
06/11/2025









