As a personnel who has long been involved in the operation and maintenance projects of power distribution equipment, I deeply recognize that distribution transformers, situated in the complex power distribution ecosystem, continuously endure mechanical stresses from electromagnetic forces caused by electrical faults, vibrations during transportation, and various environmental forces. To ensure their mechanical integrity, systematic inspections are indispensable. Different from electrical and thermal performance evaluations, mechanical performance inspections focus on structural durability, which is the key to preventing catastrophic failures. Below, from the perspective of practical work, I sort out the key points of mechanical testing for distribution transformers.
I. Understanding the Necessity of Mechanical Inspections
In daily operation and maintenance, I am well aware that distribution transformers face mechanical challenges throughout their entire life cycle from commissioning to decommissioning. The powerful electromagnetic forces generated by short circuits may deform the windings; seismic activities or rough handling during transportation can also damage internal components. Therefore, regular inspection work, ranging from simple visual inspections to complex dynamic tests, can help us detect hidden defects in the equipment. By identifying mechanical weak points as early as possible, operation and maintenance personnel can intervene in advance to avoid sudden failures, prevent power supply interruptions, and protect the safety of infrastructure.
II. Implementation of Core Mechanical Test Contents
(1) Short - Circuit Impulse Test
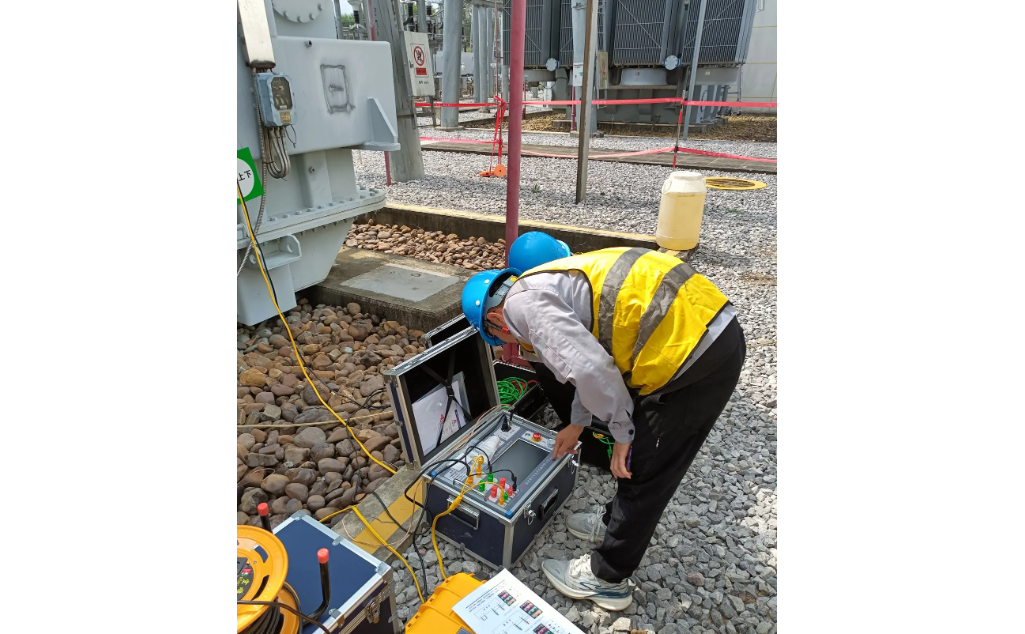
During work, I will carry out short - circuit impulse tests to simulate fault conditions and thus measure the transformer's ability to withstand electromagnetic forces. During the test, if a deviation in impedance or a displacement of the windings is detected, it indicates that there is mechanical stress in the equipment. At this time, I will arrange an inspection of the clamping structure and the support frame to identify potential problems.
(2) Vibration Analysis Inspection
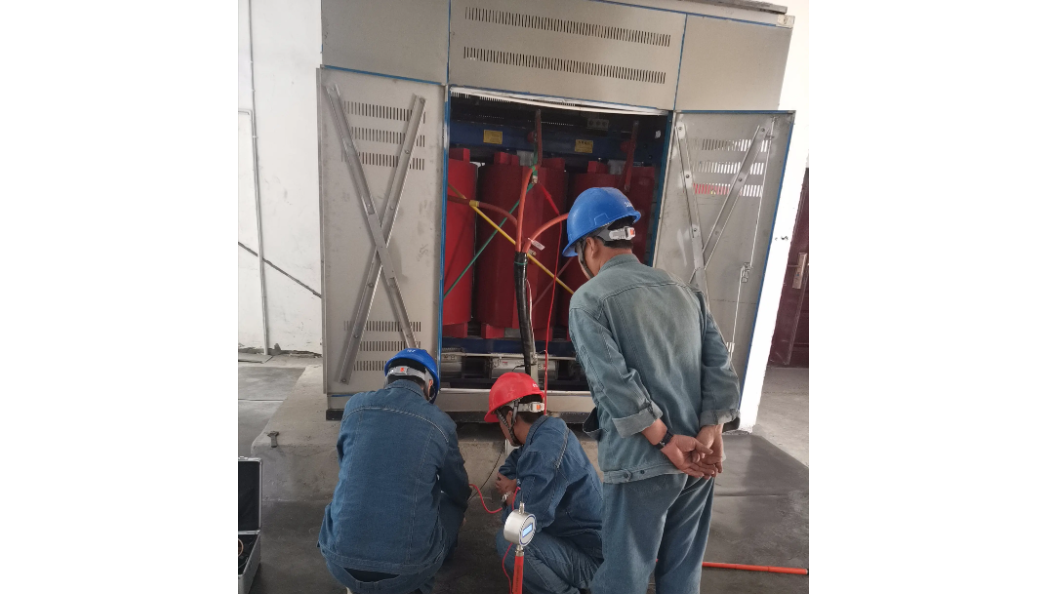
During operation and maintenance, sensors can be used to monitor the vibration of the equipment during operation. Once an abnormal frequency is detected, it is very likely that there are problems such as loose components, misaligned iron cores, or damaged cooling fans in the equipment. This non - invasive inspection method allows me to accurately locate and carry out repair work before the mechanical problems worsen, ensuring the stable operation of the equipment.
(3) Mechanical Impact Test
For newly produced or transported transformers, I will conduct mechanical impact tests to evaluate their ability to withstand impacts. Through methods such as drop tests and seismic simulations, the weak points of parts such as the oil tank, bushings, or terminal connections are exposed, and then an inspection of key joints is triggered to control the equipment quality from the source.
III. Compliance with Inspection Procedures and Standards
During the testing process, it is necessary to strictly carry out strict mechanical inspections in accordance with standards such as IEEE C57.12.90 and IEC 61378. Follow precise procedures. For example, when conducting a short - circuit test, while monitoring the mechanical response, accurately control the current injection. After each inspection, carefully record the test parameters, observed deformation conditions, and maintenance suggestions, and establish historical records to provide data support for subsequent equipment analysis.
IV. Strategies for Adapting Inspection Frequency to Scenarios
Based on the actual work scenarios, I flexibly adjust the frequency of mechanical inspections. In earthquake - prone areas, a vibration inspection is carried out on distribution transformers quarterly; in stable environmental areas, an annual inspection is sufficient. Immediately after the transportation of newly installed equipment, an inspection is carried out to verify its integrity. At the same time, using advanced monitoring systems, through embedded strain gauges and accelerometers, the continuous inspection of the mechanical performance of the equipment is realized, and the operation and maintenance efficiency is improved.
V. Methods to Overcome Inspection Difficulties
In actual work, mechanical inspections will encounter many complex problems, such as detecting internal damage without disassembling the equipment. For such situations, when professional inspection methods such as ultrasonic testing are involved, I will carry out the work relying on professional knowledge. In addition, distinguishing between normal wear and abnormal deterioration requires experience - based judgment. I usually combine multiple inspection methods, such as combining vibration analysis with visual inspection, and at the same time use historical data for comparative evaluation to improve the accuracy of inspections.
VI. Integrated Practice of Mechanical Inspection and Maintenance
In the operation and maintenance process, mechanical inspection is a key link connecting diagnosis and maintenance actions. A comprehensive inspection report, which marks problems such as loose bolts, deformed windings, or damaged support components of the equipment, can clarify the needs for emergency repairs or component replacement. For example, if a misaligned iron core is found during a vibration inspection, realigning and tightening will be the top priority. Incorporating mechanical inspections into the preventive maintenance plan can effectively extend the service life of the transformer and enhance the resilience of the power grid.
In conclusion, from the perspective of actual operation and maintenance, mechanical performance inspection is an important means to protect distribution transformers from structural damage. Through standardized testing, data - driven analysis, and proactive intervention, transformers are guaranteed to withstand mechanical tests. With the changes in power demand, giving priority to carrying out comprehensive mechanical inspections is the best practice in operation and is also the key to maintaining the reliable operation of the power grid.