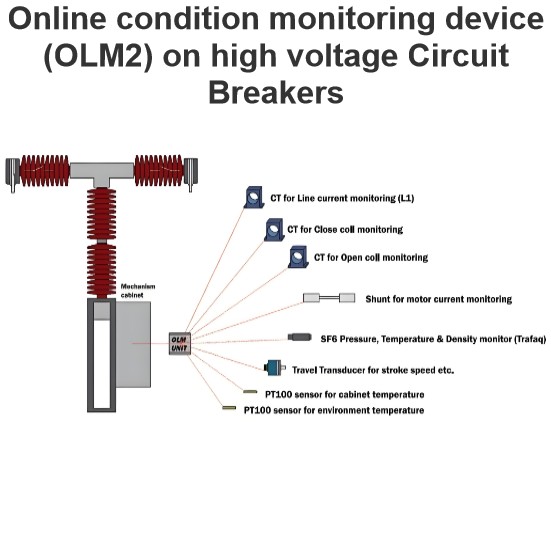
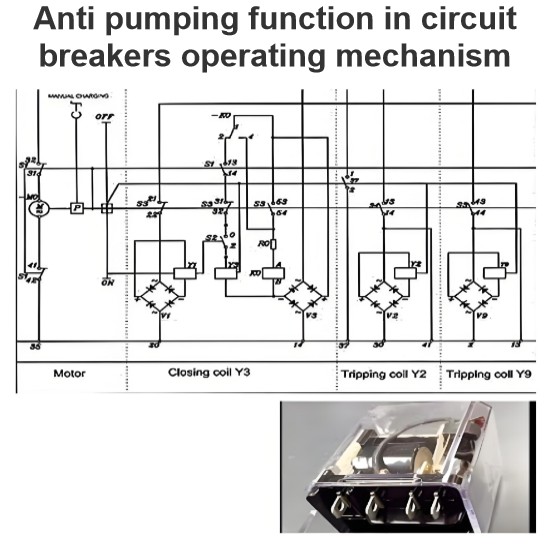
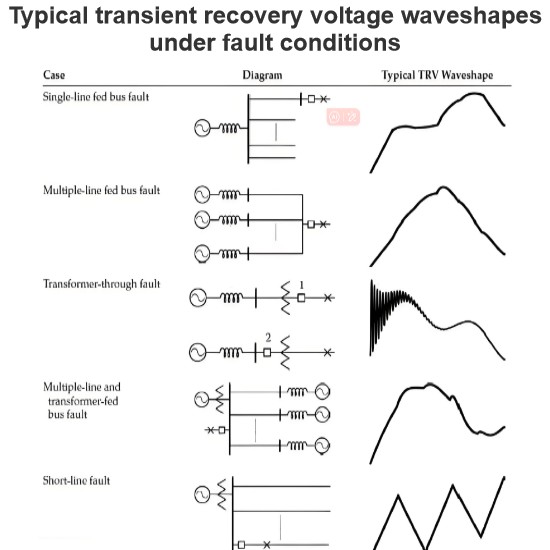
Initial Transient Recovery Voltage (ITRV) for high voltage circuit breakers
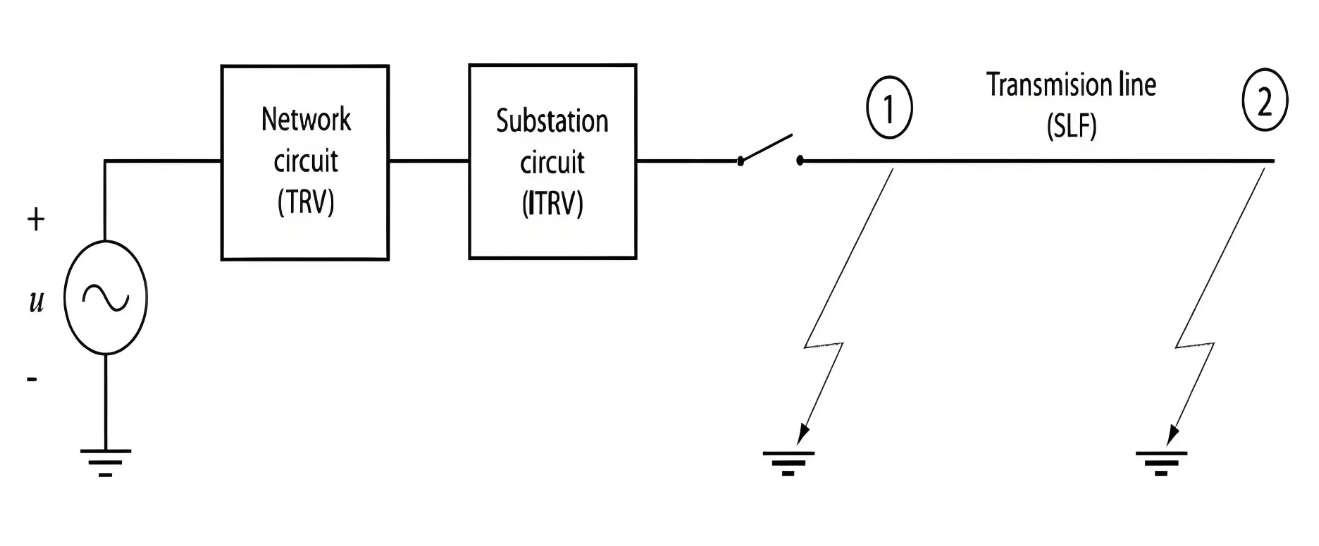
Transient Recovery Voltage (TRV) stress similar to that encountered during a short-line fault can also occur due to the busbar connections on the supply side of a circuit breaker. This specific TRV stress is known as Initial Transient Recovery Voltage (ITRV). Given the relatively short distances involved, the time to reach the first peak of ITRV is typically less than 1 microsecond. The surge impedance of the busbars within a substation is generally lower compared to that of overhead lines.
The figure illustrates the origins of the different contributions to the total recovery voltage for terminal faults and short-line faults: ITRV, and the TRV for terminal fault (1), and for short-line fault (2). At the source side of the circuit breaker, the TRV originates from the supply network, while the substation topology, primarily the busbars, generates the ITRV oscillation. In the case of a short-line fault, the total recovery voltage consists of three components:
- TRV (Network) - Generated by the supply network.
- ITRV (Substation) - Caused by the substation's internal layout, mainly involving the busbars.
- Line Oscillation - Resulting from the characteristics of the transmission line itself.
Understanding these components is crucial for assessing the overall voltage stress on circuit breakers and other equipment during fault conditions, aiding in the design and selection of appropriate protective measures and devices. This comprehensive analysis helps ensure the reliability and safety of electrical power systems.