What is Power System Stability?
What is Power System Stability?
Power System Stability Definition
Power system stability is defined as the ability of an electrical system to return to steady-state operation after a disturbance.
Importance of Stability
Ensuring power system stability is crucial for maintaining a reliable and uninterrupted power supply.
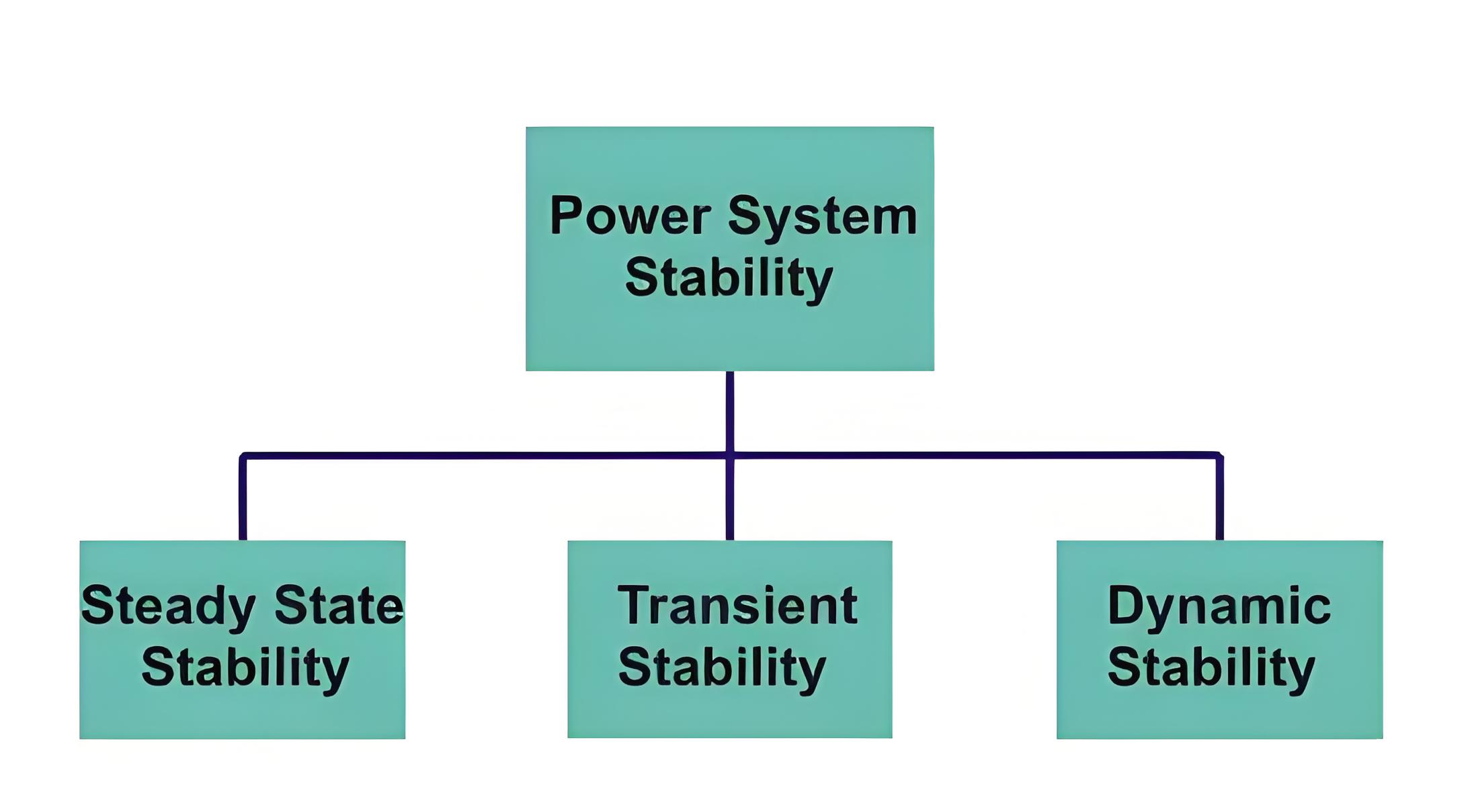
The power system stability or synchronous stability of a power system can be of several types depending upon the nature of the disturbance, and for successful analysis, it can be classified into the following three types as shown below:
Steady state stability
Transient stability
Dynamic stability
Synchronous Stability
This is the system’s ability to maintain synchronism between all generators and the grid during disturbances.
Steady State Stability
Refers to the system’s ability to recover from small disturbances, such as minor load changes.
Transient Stability
Refers to the system’s ability to remain stable after significant disturbances, like sudden load changes or faults.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.