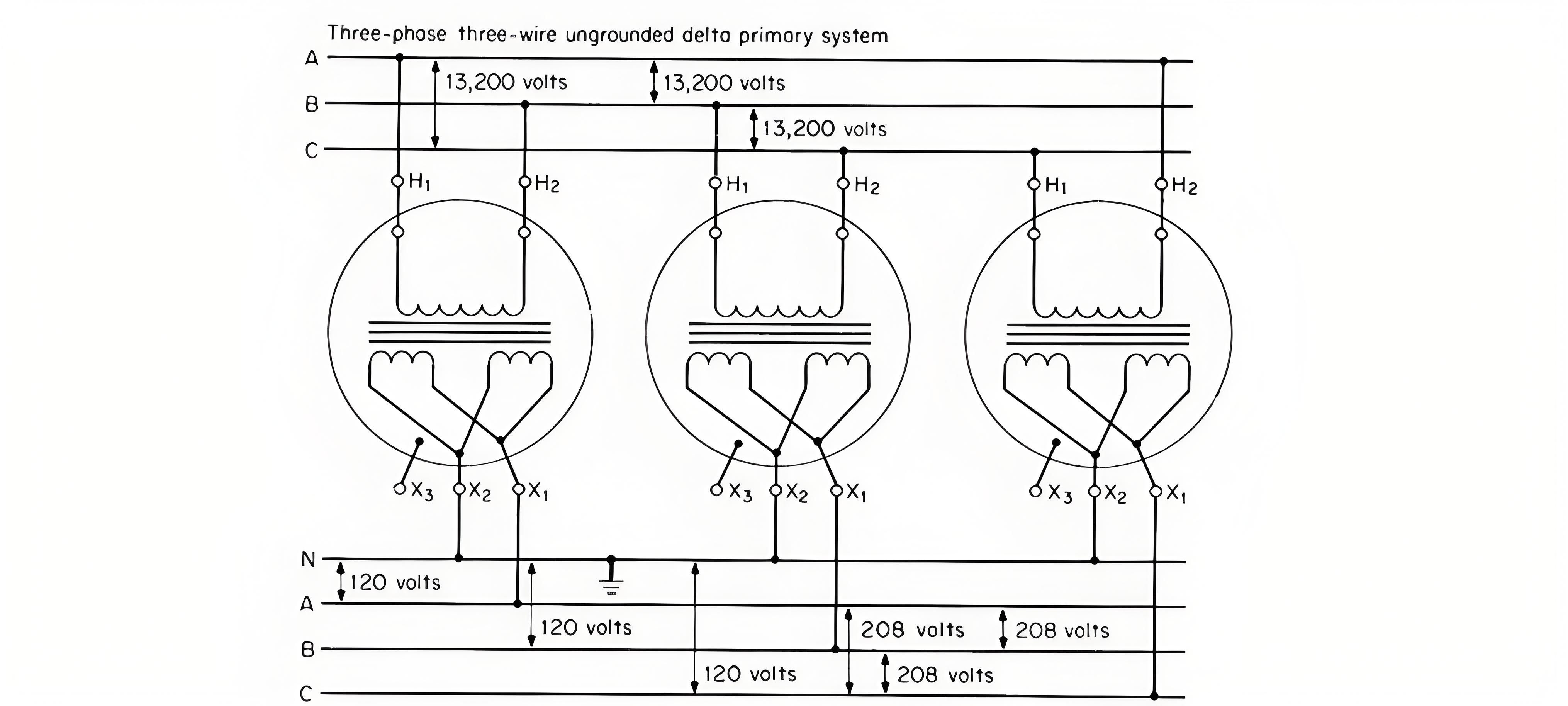
Grounding connections
Most network transformers are connected delta – grounded wye.By blocking the zero - sequence current, this connection keeps the grounding current on the primary cables at a low level. Consequently, a highly - sensitive ground - fault relay can be employed on the substation circuit breaker. Blocking the zero - sequence current also reduces the current on the cable neutrals and cable sheaths, including zero - sequence harmonics, predominantly the third harmonic.In the event of a primary line - to - ground fault, the feeder circuit breaker trips, yet the network transformers will continue to backfeed the fault until all network protectors operate (and some may malfunction). At this point, the network transformers backfeed the primary feeder as an ungrounded circuit.
In an ungrounded circuit, a single - phase line - to - ground fault causes a neutral - point shift, which raises the phase - to - neutral voltage of the unfaulted phases to the phase - to - phase voltage level. Non - network loads connected phase - to - neutral will be exposed to this overvoltage.Some networks adopt the grounded wye - grounded wye connection method.
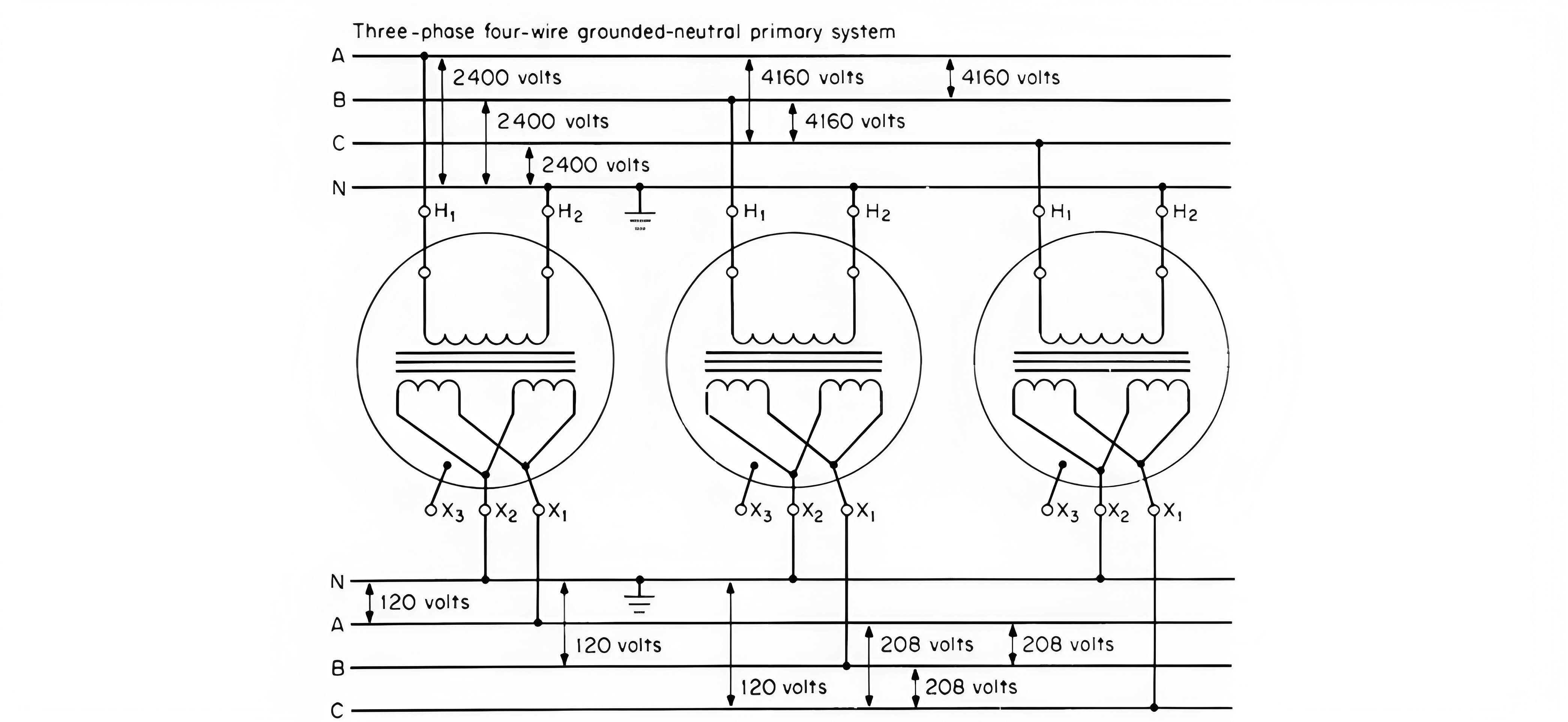
This connection is more suitable for combination feeders. In the event of a primary line - to - ground fault, the feeder circuit breaker trips. For the backfeed current to the primary through the network, the wye - wye connection still provides a grounding reference point, thus reducing the likelihood of overvoltage.The grounded wye - grounded wye connection also decreases the probability of ferroresonance when the transformer undergoes single - pole switching.
Most network transformers are of the core type, with the core structure being either three - legged (three - phase, three - column) or five - legged (three - phase, five - column). The three - legged core, whether it is a stacked core or a wound core, is suitable for a delta - grounded wye connection (but not for a grounded wye - grounded wye connection due to tank heating issues). A five - legged core transformer is suitable for both of the above - mentioned connection types.