Parallel Magnetic Circuit MMF Calculation
Thus, the total magnetomotive force (MMF) or ampere-turns required for a parallel magnetic circuit equals the MMF of any single parallel path, as all branches experience the same applied MMF.
Incorrect Notation Clarification:
The total MMF is not the sum of individual paths (a common misconception). Instead, since parallel magnetic paths share the same applied MMF, the correct relation is:
Total MMF = MMF for path BA = MMF for path ADCB = MMF for path AFEB
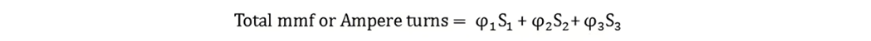
Where φ1. Φ2, φ3 is the flux and S1, S2, S3 are the reluctances of the parallel path BA, ADCB and AFEB respectively.