Leakage Flux and Fringing Effect Analysis
Definition: Leakage flux refers to the magnetic flux that deviates from the intended path in a magnetic circuit. This can be illustrated using a solenoid to distinguish between leakage flux and fringing effect:
When current passes through a solenoid, most flux forms the main flux along the core axis, while a fraction leaks outside the coil without fully following the core path—this is leakage flux. In a long solenoid, leakage flux primarily occurs at both ends, where magnetic field lines diverge into the surrounding air instead of passing through the core's cross - section.
Simultaneously, at the solenoid's ends, magnetic field lines exhibit non - uniform distribution, creating a "fringing effect" that causes flux diffusion. Unlike leakage flux (which emphasizes path deviation), fringing describes the main flux's dispersion at boundaries. Both phenomena impact solenoid efficiency: leakage flux induces energy loss, while fringing distorts the magnetic field, requiring optimization through measures like increasing core cross - section or applying magnetic shielding in electromagnetic designs.
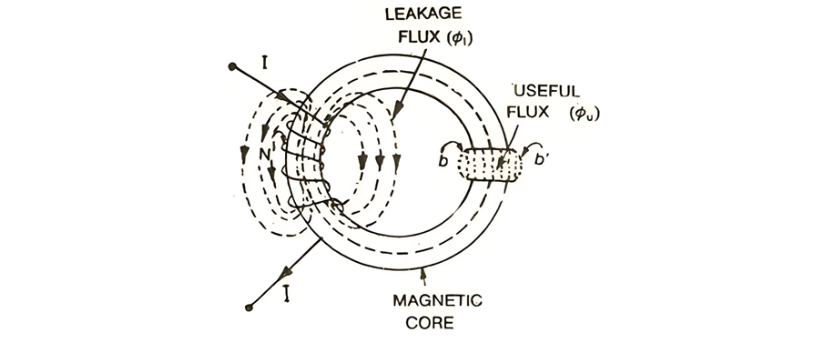
Flux Classification in Solenoid Magnetic Circuits
The majority of magnetic flux generated by a solenoid propagates through the core, traverses the air gap, and contributes to the magnetic circuit's intended function. This component is defined as the useful flux (φᵤ).
In practical scenarios, not all flux adheres strictly to the designed path within the magnetic core. A portion of the flux emanates around the coil or surrounds the core without contributing to the circuit's operational purpose. This non - functional flux is termed leakage flux (φₗ), which dissipates in the surrounding medium rather than participating in electromagnetic work.
Consequently, the total flux (Φ) produced by the solenoid is the algebraic sum of useful and leakage flux components, expressed by the equation:Φ= ϕu + ϕl
Leakage coefficient The ratio of the total flux produced to the useful flux set up in the air gap of the magnetic circuit is called a leakage coefficient or leakage factor. It is denoted by (λ).