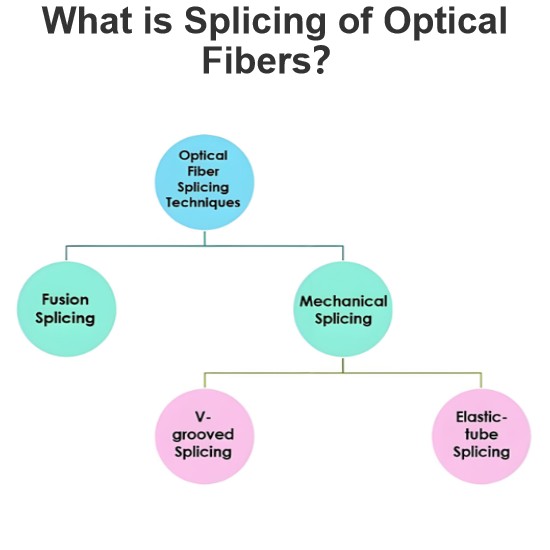
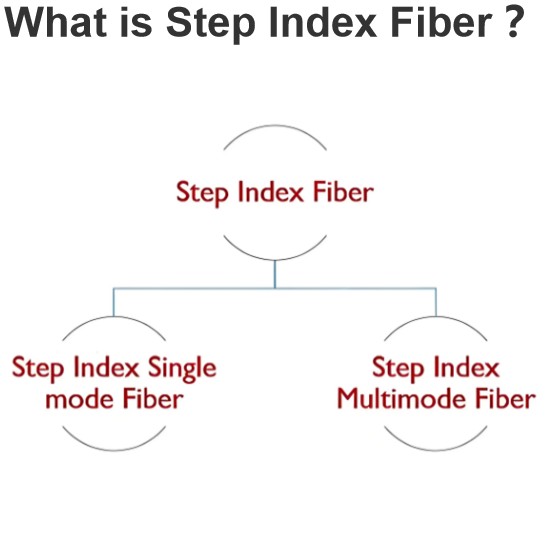
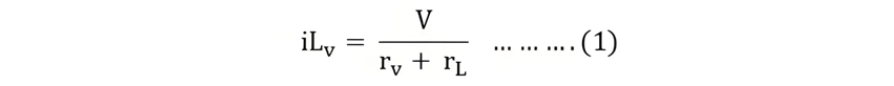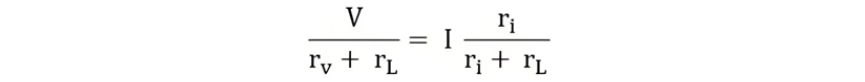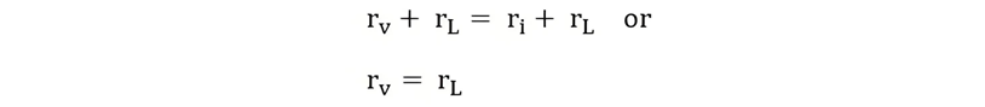Source Transformation
Source transformation refers to replacing one type of electrical source with an equivalent alternative. A practical voltage source can be converted into an equivalent practical current source, and vice versa.
Practical Voltage Source
A practical voltage source consists of an ideal voltage source in series with an internal resistance (or impedance, for AC circuits). For an ideal voltage source, this internal impedance is zero, meaning the output voltage remains constant regardless of the load current. Examples include cells, batteries, and generators.
Practical Current Source
A practical current source comprises an ideal current source in parallel with an internal resistance (or impedance). For an ideal current source, this parallel impedance is infinite, ensuring the output current remains constant irrespective of the load voltage. Semiconductor devices like transistors are often modeled as current sources. Outputs from DC or AC voltage sources are referred to as direct or alternating current sources, respectively.
Mutual Transformability
Voltage and current sources are mutually transformable through source transformation. To illustrate, consider the circuit below:
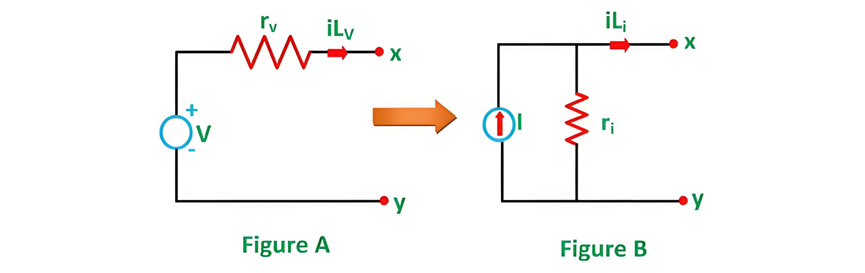
Figure A shows a practical voltage source in series with an internal resistance rv, while Figure B depicts a practical current source with a parallel internal resistance ri.
For the practical voltage source, the load current is given by the equation:
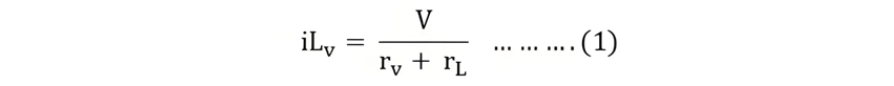
Where,
- iLv is the load current for the practical voltage source
- V is the voltage
- rv is the internal resistance of the voltage source
- rL is the load resistance
It is assumed that a load resistance rL is connected across the terminals x-y. Similarly, for the practical current source, the load current is given by:
- iLi is the load current for the practical current source
- I is the current
- ri is the internal resistance of the current source
- rL is the load resistance connected across the terminal x-y in the figure B
Two sources become identical, when we will equate equation (1) and equation (2)
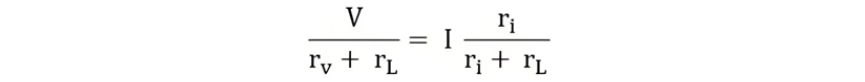
However, for the current source, when the terminals x-y are open (no load connected), the terminal voltage at x-y is V = I ×ri. Therefore, we obtain:
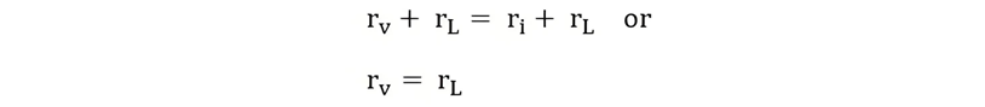
Therefore, for any practical voltage source with an ideal voltage V and internal resistance rv, the voltage source can be replaced by a current source I with the internal resistance connected in parallel with the current source.
Source Transformation: Conversion of Voltage Source into Current Source

When a voltage source is in series with a resistance and needs to be converted into a current source, the resistance is connected in parallel with the current source, as illustrated in the figure above. Here, the current source value is given by:Is=Vs/R
Conversion of Current Source into Voltage Source
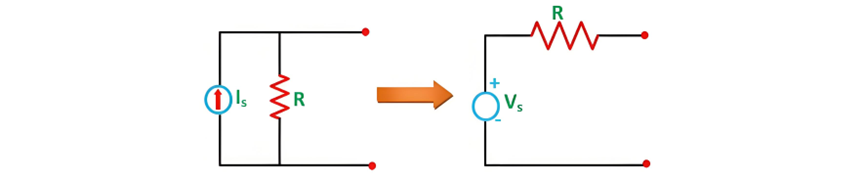
In the circuit diagram above, a current source connected in parallel with a resistance can be transformed into a voltage source by placing the resistance in series with the voltage source. Here, the voltage source value is given by:Vs = Is × R